Chk2-dependent HuR phosphorylation regulates occludin mRNA translation and epithelial barrier function
- PMID: 21745814
- PMCID: PMC3201881
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr567
Chk2-dependent HuR phosphorylation regulates occludin mRNA translation and epithelial barrier function
Abstract
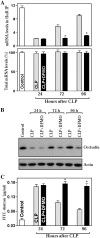
Occludin is a transmembrane tight junction (TJ) protein that plays an important role in TJ assembly and regulation of the epithelial barrier function, but the mechanisms underlying its post-transcriptional regulation are unknown. The RNA-binding protein HuR modulates the stability and translation of many target mRNAs. Here, we investigated the role of HuR in the regulation of occludin expression and therefore in the intestinal epithelial barrier function. HuR bound the 3'-untranslated region of the occludin mRNA and enhanced occludin translation. HuR association with the occludin mRNA depended on Chk2-dependent HuR phosphorylation. Reduced HuR phosphorylation by Chk2 silencing or by reduction of Chk2 through polyamine depletion decreased HuR-binding to the occludin mRNA and repressed occludin translation, whereas Chk2 overexpression enhanced (HuR/occludin mRNA) association and stimulated occludin expression. In mice exposed to septic stress induced by cecal ligation and puncture, Chk2 levels in the intestinal mucosa decreased, associated with an inhibition of occludin expression and gut barrier dysfunction. These results indicate that HuR regulates occludin mRNA translation through Chk2-dependent HuR phosphorylation and that this influence is crucial for maintenance of the epithelial barrier integrity in the intestinal tract.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Stabilization of Cx43 mRNA via RNA-binding protein HuR regulated by polyamines enhances intestinal epithelial barrier function.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023 Dec 1;325(6):G518-G527. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00143.2023. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37788332 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamines regulate c-Myc translation through Chk2-dependent HuR phosphorylation.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Dec;20(23):4885-98. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-07-0550. Epub 2009 Oct 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19812253 Free PMC article.
-
Competitive binding of CUGBP1 and HuR to occludin mRNA controls its translation and modulates epithelial barrier function.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Jan;24(2):85-99. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-07-0531. Epub 2012 Nov 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23155001 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the mRNA-binding protein HuR by posttranslational modification: spotlight on phosphorylation.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012 Jun;13(4):380-90. doi: 10.2174/138920312801619439. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 22708484 Review.
-
Properties of the Regulatory RNA-Binding Protein HuR and its Role in Controlling miRNA Repression.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;700:106-23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-7823-3_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21755477 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of Wnt co-receptor LRP6 and RNA-binding protein HuR by miR-29b in intestinal epithelial cells.Biochem J. 2016 Jun 1;473(11):1641-9. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160057. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27089893 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA H19 Impairs the Intestinal Barrier by Suppressing Autophagy and Lowering Paneth and Goblet Cell Function.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;9(4):611-625. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.12.002. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31862317 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Effects of Metabolites on the Gut Microbiome and Severe Acute Pancreatitis.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Oct 19;2021:1516855. doi: 10.1155/2021/1516855. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34712726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long noncoding RNA SPRY4-IT1 regulates intestinal epithelial barrier function by modulating the expression levels of tight junction proteins.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Feb 15;27(4):617-26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-10-0703. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26680741 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization of Cx43 mRNA via RNA-binding protein HuR regulated by polyamines enhances intestinal epithelial barrier function.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023 Dec 1;325(6):G518-G527. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00143.2023. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37788332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Turner JR. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009;9:799–809. - PubMed
-
- Schulzke JD, Fromm M. Tight junctions: molecular structure meets function. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2009;1165:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Funke L, Dakoji S, Bredt DS. Membrane-associated guanylate kinases regulate adhesion and plasticity at cell junctions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2005;74:219–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

