Lessons from morpholino-based screening in zebrafish
- PMID: 21746693
- PMCID: PMC3144740
- DOI: 10.1093/bfgp/elr021
Lessons from morpholino-based screening in zebrafish
Abstract
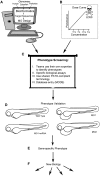
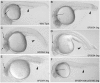
Morpholino oligonucleotides (MOs) are an effective, gene-specific antisense knockdown technology used in many model systems. Here we describe the application of MOs in zebrafish (Danio rerio) for in vivo functional characterization of gene activity. We summarize our screening experience beginning with gene target selection. We then discuss screening parameter considerations and data and database management. Finally, we emphasize the importance of off-target effect management and thorough downstream phenotypic validation. We discuss current morpholino limitations, including reduced stability when stored in aqueous solution. Advances in MO technology now provide a measure of spatiotemporal control over MO activity, presenting the opportunity for incorporating more finely tuned analyses into MO-based screening. Therefore, with careful management, MOs remain a valuable tool for discovery screening as well as individual gene knockdown analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Barstead R. Genome-wide RNAi. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2001;5:63–6. - PubMed
-
- Lum L, Yao S, Mozer B, et al. Identification of Hedgehog pathway components by RNAi in Drosophila cultured cells. Science. 2003;299:2039–45. - PubMed
-
- Eisen JS, Smith JC. Controlling morpholino experiments: don’t stop making antisense. Development. 2008;135:1735–43. - PubMed
-
- Summerton J, Weller D. Morpholino antisense oligomers: design, preparation, and properties. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1997;7:187–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

