Hippocampal sclerosis in temporal lobe epilepsy: findings at 7 T¹
- PMID: 21746814
- PMCID: PMC3176424
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.11101651
Hippocampal sclerosis in temporal lobe epilepsy: findings at 7 T¹
Abstract
Purpose: To determine if ultrahigh-field-strength magnetic resonance (MR) imaging can be used to detect subregional hippocampal alterations.
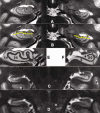
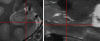
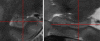
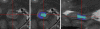
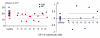
Materials and methods: Subjects provided written consent to participate in this prospective institutional review board-approved HIPAA-compliant study. T1- and T2-weighted 7-T brain MR images were acquired in 11 healthy subjects and eight patients with temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE). In all subjects, images were qualitatively examined for evidence of hippocampal atrophy, signal change, and malrotation with the Bernasconi definition, and digitations of the hippocampal heads were counted (agreement was measured with the κ statistic). Data were analyzed quantitatively with manual subregional hippocampal body segmentation. Subregional data in individual subjects with TLE were compared with data in control subjects to detect deviation from the control range for volume measures on each side and with asymmetry indexes.
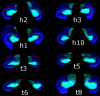
Results: All eight patients with TLE had hippocampal abnormalities on the epileptogenic side. Subregional analysis revealed selective lateral Ammon horn atrophy in six patients and diffuse Ammon horn and dentate gyrus atrophy in one patient. Paucity of hippocampal digitations occurred on the epileptogenic side in all patients with TLE and also on the contralateral side in three patients (interrater κ value, 0.80). Hippocampal malrotation was observed in three patients with TLE and four control subjects.
Conclusion: Ultrahigh-field-strength MR imaging permitted detection of selectively greater Ammon horn atrophy in patients with TLE and hippocampal sclerosis. Paucity of digitations is a deformity of the hippocampal head that was detected independent of hippocampal atrophy in patients with mesial TLE.
© RSNA, 2011.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Subfield atrophy pattern in temporal lobe epilepsy with and without mesial sclerosis detected by high-resolution MRI at 4 Tesla: preliminary results.Epilepsia. 2009 Jun;50(6):1474-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02010.x. Epub 2009 Mar 12. Epilepsia. 2009. PMID: 19400880 Free PMC article.
-
[Qualitative and quantitative MRI findings in temporal lobe epilepsy].Tani Girisim Radyol. 2003 Jun;9(2):157-65. Tani Girisim Radyol. 2003. PMID: 14661482 Turkish.
-
T2 hyperintense signal in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy with MRI signs of hippocampal sclerosis and in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy with normal MRI.Epilepsy Behav. 2015 May;46:103-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 May 1. Epilepsy Behav. 2015. PMID: 25936278
-
[Magnetic resonance imaging of temporal lobe epilepsy].J Radiol. 1996 Nov;77(11):1095-104. J Radiol. 1996. PMID: 9033867 Review. French.
-
Hippocampal sclerosis: histopathology substrate and magnetic resonance imaging.Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2008 Feb;29(1):2-14. doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2007.11.005. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2008. PMID: 18383904 Review.
Cited by
-
Phase-based fast 3D high-resolution quantitative T2 MRI in 7 T human brain imaging.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 18;12(1):14088. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17607-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35982143 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging at ultrahigh magnetic fields: History, challenges, and solutions.Neuroimage. 2018 Mar;168:7-32. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Jul 8. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 28698108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: A West Indian Neurosurgical Experience.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019;65:275-278. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.10.063. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31756688 Free PMC article.
-
Balancing Clinical and Pathologic Relevence in the Machine Learning Diagnosis of Epilepsy.Int Workshop Pattern Recognit Neuroimaging. 2013 Jun;2013:86-89. doi: 10.1109/PRNI.2013.31. Int Workshop Pattern Recognit Neuroimaging. 2013. PMID: 25302313 Free PMC article.
-
7T Epilepsy Task Force Consensus Recommendations on the Use of 7T MRI in Clinical Practice.Neurology. 2021 Feb 16;96(7):327-341. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000011413. Epub 2020 Dec 22. Neurology. 2021. PMID: 33361257 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Engel J., Jr Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: what have we learned? Neuroscientist 2001;7(4):340–352 - PubMed
-
- Bruton CJ. The neuropathology of temporal lobe epilepsy. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 1988
-
- Margerison JH, Corsellis JA. Epilepsy and the temporal lobes. A clinical, electroencephalographic and neuropathological study of the brain in epilepsy, with particular reference to the temporal lobes. Brain 1966;89(3):499–530 - PubMed
-
- Babb TL, Brown WJ, Pretorius J, Davenport C, Lieb JP, Crandall PH. Temporal lobe volumetric cell densities in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 1984;25(6):729–740 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

