Increased survival and reduced neutrophil infiltration of the liver in Rab27a- but not Munc13-4-deficient mice in lipopolysaccharide-induced systemic inflammation
- PMID: 21746860
- PMCID: PMC3165471
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.05043-11
Increased survival and reduced neutrophil infiltration of the liver in Rab27a- but not Munc13-4-deficient mice in lipopolysaccharide-induced systemic inflammation
Abstract
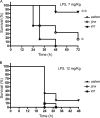
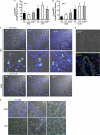
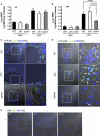
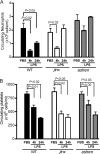
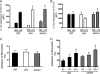
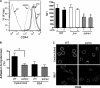
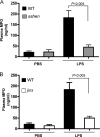
Genetic defects in the Rab27a or Munc13-4 gene lead to immunodeficiencies in humans, characterized by frequent viral and bacterial infections. However, the role of Rab27a and Munc13-4 in the regulation of systemic inflammation initiated by Gram-negative bacterium-derived pathogenic molecules is currently unknown. Using a model of lipopolysaccharide-induced systemic inflammation, we show that Rab27a-deficient (Rab27a(ash/ash)) mice are resistant to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced death, while Munc13-4-deficient (Munc13-4(jinx/jinx)) mice show only moderate protection. Rab27a(ash/ash) but not Munc13-4(jinx/jinx) mice showed significantly decreased tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) plasma levels after LPS administration. Neutrophil sequestration in lungs from Rab27a(ash/ash) and Munc13-4(jinx/jinx) LPS-treated mice was similar to that observed for wild-type mice. In contrast, Rab27a- but not Munc13-4-deficient mice showed decreased neutrophil infiltration in liver and failed to undergo LPS-induced neutropenia. Decreased liver infiltration in Rab27a(ash/ash) mice was accompanied by lower CD44 but normal CD11a and CD11b expression in neutrophils. Both Rab27a- and Munc13-4-deficient mice showed decreased azurophilic granule secretion in vivo, suggesting that impaired liver infiltration and improved survival in Rab27a(ash/ash) mice is not fully explained by deficient exocytosis of this granule subset. Altogether, our data indicate that Rab27a but not Munc13-4 plays an important role in neutrophil recruitment to liver and LPS-induced death during endotoxemia, thus highlighting a previously unrecognized role for Rab27a in LPS-mediated systemic inflammation.
Figures

References
-
- Basit A., et al. 2006. ICAM-1 and LFA-1 play critical roles in LPS-induced neutrophil recruitment into the alveolar space. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 291:L200–L207 - PubMed
-
- Beck-Schimmer B., et al. 2002. Role of alveolar epithelial ICAM-1 in lipopolysaccharide-induced lung inflammation. Eur. Respir. J. 19:1142–1150 - PubMed
-
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. 1985. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science 229:869–871 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

