Mutation of RNA polymerase beta subunit (rpoB) promotes hVISA-to-VISA phenotypic conversion of strain Mu3
- PMID: 21746940
- PMCID: PMC3165293
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00398-11
Mutation of RNA polymerase beta subunit (rpoB) promotes hVISA-to-VISA phenotypic conversion of strain Mu3
Abstract
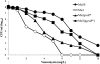
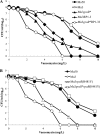
The clinical vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA) strain Mu50 carries two mutations in the vraSR and graRS two-component regulatory systems (TCRSs), namely, vraS(I5N) and graR(N197S) (hereinafter designated graR). The clinical heterogeneously vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus (hVISA) strain Mu3 shares with Mu50 the mutation in vraS that encodes the VraS two-component histidine kinase. Previously, we showed that introduction of the plasmid pgraR, carrying the mutated two-component response regulator graR, converted the hVISA strain Mu3 into VISA (vancomycin MIC = 4 mg/liter). Subsequently, however, we found that the introduction of a single copy of graR into the Mu3 chromosome by a gene replacement method did not confer on Mu3 the VISA phenotype. The gene-replaced strain Mu3graR thus obtained remained hVISA (MIC ≤ 2 mg/liter), although a small increase in vancomycin MIC was observed compared to that of the parent strain Mu3. Reevaluation of the Mu3 and Mu50 genomes revealed the presence of another mutation responsible for the expression of the VISA phenotype in Mu50. Here, we demonstrate that in addition to the two regulator mutations, a third mutation found in the Mu50 rpoB gene, encoding the RNA polymerase β subunit, was required for Mu3 to achieve the level of vancomycin resistance of Mu50. The selection of strain Mu3graR with rifampin gave rise to rpoB mutants with various levels of increased vancomycin resistance. Furthermore, 3 (33%) of 10 independently isolated VISA strains established from the heterogeneous subpopulations of Mu3graR were found to possess rpoB mutations with or without an accompanying rifampin-resistance phenotype. The data indicate that a sizable proportion of the resistant hVISA cell subpopulations is composed of spontaneous rpoB mutants with various degrees of increased vancomycin resistance.
Figures
References
-
- Bae T., Schneewind O. 2006. Allelic replacement in Staphylococcus aureus with inducible counter-selection. Plasmid 55:58–63 - PubMed
-
- Campbell E. A., et al. 2001. Structural mechanism for rifampicin inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase. Cell 104:901–912 - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2009. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically, 8th ed., vol. 29, no. 2 Approved standard M07-A8. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

