Spread of ISCR1 elements containing blaDHA-₁ and multiple antimicrobial resistance genes leading to increase of flomoxef resistance in extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 21746945
- PMCID: PMC3165323
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00259-11
Spread of ISCR1 elements containing blaDHA-₁ and multiple antimicrobial resistance genes leading to increase of flomoxef resistance in extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
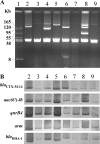
Increasing resistance to quinolones, aminoglycosides, and/or cephamycins in extended-spectrum-β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae exacerbates the already limited antibiotic treatment options for infections due to these microbes. In this study, the presence of resistance determinants for these antimicrobial agents was examined by PCR among ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (ESBL-KP) isolates that caused bacteremia. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis was used to differentiate the clonal relationship among the isolates studied. Transferability and the location of the resistance genes were analyzed by conjugation experiments, followed by DNA-DNA hybridization. Among the 94 ESBL-KP isolates studied, 20 isolates of flomoxef-resistant ESBL-KP were identified. They all carried a DHA-1 gene and were genetically diverse. CTX-M genes were found in 18 of the isolates. Among these DHA-1/CTX-M-producing K. pneumoniae isolates, ISCR1 was detected in 13 (72%) isolates, qnr genes (1 qnrA and 17 qnrB genes) were detected in 18 (100%), aac(6')-Ib-cr was detected in 11 (61%), and 16S rRNA methylase (all armA genes) was detected in 14 (78%). Four transconjugants were available for further analysis, and qnrB4, aac(6')-Ib-cr, armA, and bla(DHA-1) were all identified on these self-transferable bla(CTX-M)-carrying plasmids. The genetic environments of ISCR1 associated with armA, bla(DHA-1), and qnrB4 genes in the four transconjugants were identical. Replicon-type analysis revealed a FIIA plasmid among the four self-transferable plasmids, although the other three were nontypeable. The cotransfer of multiple resistance genes with the ISCR1 element-carrying plasmids has a clinical impact and warrants close monitoring and further study.
Figures
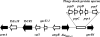
Similar articles
-
Co-production of SFO-1 and DHA-1 β-lactamases and 16S rRNA methylase ArmA in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012 Oct;67(10):2361-6. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks244. Epub 2012 Jul 9. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22778158
-
Characterization of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase, carbapenemase, and plasmid quinolone determinants in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates carrying distinct types of 16S rRNA methylase genes, and their association with mobile genetic elements.Microb Drug Resist. 2015 Apr;21(2):186-93. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2014.0073. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Microb Drug Resist. 2015. PMID: 25469905
-
Molecular epidemiology of ciprofloxacin-resistant extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan.Microb Drug Resist. 2012 Feb;18(1):52-8. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2011.0060. Epub 2011 Oct 24. Microb Drug Resist. 2012. PMID: 22022870
-
Prevalence of β-lactamases and 16S rRNA methylase genes amongst clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates carrying plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011 Apr;37(4):352-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.12.018. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011. PMID: 21376540
-
Plasmids carrying DHA-1 β-lactamases.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018 Jul;37(7):1197-1209. doi: 10.1007/s10096-018-3231-9. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29663096 Review.
Cited by
-
Flomoxef and fosfomycin in combination for the treatment of neonatal sepsis in the setting of highly prevalent antimicrobial resistance.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022 Apr 27;77(5):1334-1343. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkac038. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022. PMID: 35170719 Free PMC article.
-
Clonal Spread of 16S rRNA Methyltransferase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST37 with High Prevalence of ESBLs from Companion Animals in China.Front Microbiol. 2017 Mar 29;8:529. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00529. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28446899 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Antibiotics for the Treatment of Neonatal Sepsis Caused by Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria.Paediatr Drugs. 2021 Sep;23(5):465-484. doi: 10.1007/s40272-021-00465-z. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Paediatr Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34435316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanism of the β-Lactamase Mediated β-Lactam Antibiotic Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated From a Chinese Teaching Hospital.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 28;13:855961. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.855961. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35572664 Free PMC article.
-
Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 11 from companion animals bearing ArmA methyltransferase, DHA-1 β-lactamase, and QnrB4.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Sep;57(9):4532-4. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00491-13. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23752506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambrozic Avgustin J. A., Keber R., Zerjavic K., Orazem T., Grabnar M. 2007. Emergence of the quinolone resistance-mediating gene aac(6′)-Ib-cr in extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella isolates collected in Slovenia between 2000 and 2005. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51:4171–4173 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bogaerts P., et al. 2007. Emergence of ArmA and RmtB aminoglycoside resistance 16S rRNA methylases in Belgium. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 59:459–464 - PubMed
-
- Carattoli A., et al. 2005. Identification of plasmids by PCR-based replicon typing. J. Microbiol. Methods 63:219–228 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

