Racial differences in ocular oxidative metabolism: implications for ocular disease
- PMID: 21746975
- PMCID: PMC5562541
- DOI: 10.1001/archophthalmol.2011.169
Racial differences in ocular oxidative metabolism: implications for ocular disease
Abstract
Objective: To compare the Po(2) distribution in different regions in the eyes of patients undergoing intraocular surgery.
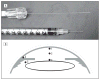
Methods: Before initiation of intraocular cataract and/or glaucoma surgery, an optical oxygen sensor was introduced into the anterior chamber via a peripheral corneal paracentesis. The tip of the flexible fiberoptic probe was positioned by the surgeon for 3 measurements in all patients: (1) near the central corneal endothelium, (2) in the mid-anterior chamber, and (3) in the anterior chamber angle. In patients scheduled to undergo cataract extraction, Po(2) was also measured (4) at the anterior lens surface and (5) in the posterior chamber just behind the iris. Oxygen measurements at the 5 locations were compared using a 2-tailed unpaired t test and multivariate regression.
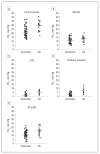
Results: The Po(2) value was significantly higher in African American patients at all 5 locations compared with Caucasian patients. Adjusting for age increased the significance of this association. Adjusting for race revealed that age was associated with increased Po(2) beneath the central cornea.
Conclusions: Racial differences in oxygen levels in the human eye reflect an important difference in oxidative metabolism in the cornea and lens and may reflect differences in systemic physiologic function. Increased oxygen or oxygen metabolites may increase oxidative stress, cell damage, intraocular pressure, and the risk of developing glaucoma. Oxygen use by the cornea decreases with age.
Figures

References
-
- Tielsch JM, Sommer A, Katz J, Royall RM, Quigley HA, Javitt J. Racial variations in the prevalence of primary open-angle glaucoma: the Baltimore Eye Survey. JAMA. 1991;266(3):369–374. - PubMed
-
- Javitt JC, McBean AM, Nicholson GA, Babish JD, Warren JL, Krakauer H. Undertreatment of glaucoma among black Americans. N Engl J Med. 1991;325(20):1418–1422. - PubMed
-
- Muñoz B, West SK, Rubin GS, et al. Causes of blindness and visual impairment in a population of older Americans: the Salisbury Eye Evaluation Study. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000;118(6):819–825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

