Reversible and regionally selective downregulation of brain cannabinoid CB1 receptors in chronic daily cannabis smokers
- PMID: 21747398
- PMCID: PMC3223558
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2011.82
Reversible and regionally selective downregulation of brain cannabinoid CB1 receptors in chronic daily cannabis smokers
Abstract
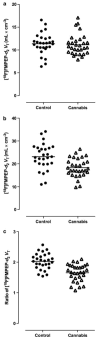
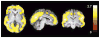
Chronic cannabis (marijuana, hashish) smoking can result in dependence. Rodent studies show reversible downregulation of brain cannabinoid CB(1) (cannabinoid receptor type 1) receptors after chronic exposure to cannabis. However, whether downregulation occurs in humans who chronically smoke cannabis is unknown. Here we show, using positron emission tomography imaging, reversible and regionally selective downregulation of brain cannabinoid CB(1) receptors in human subjects who chronically smoke cannabis. Downregulation correlated with years of cannabis smoking and was selective to cortical brain regions. After ∼4 weeks of continuously monitored abstinence from cannabis on a secure research unit, CB(1) receptor density returned to normal levels. This is the first direct demonstration of cortical cannabinoid CB(1) receptor downregulation as a neuroadaptation that may promote cannabis dependence in human brain.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Hall W, Degenhardt L. Adverse health effects of non-medical cannabis use. Lancet. 2009;374:1383–1391. - PubMed
-
- Jones RT, Benowitz NL, Herning RI. Clinical relevance of cannabis tolerance and dependence. J Clin Pharmacol. 1981;21:143S–152S. - PubMed
-
- Ramaekers JG, Kauert G, Theunissen EL, Toennes SW, Moeller MR. Neurocognitive performance during acute THC intoxication in heavy and occasional cannabis users. J Psychopharmacol. 2009;23:266–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

