Application of magnetic nanoparticles to gene delivery
- PMID: 21747701
- PMCID: PMC3131585
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms12063705
Application of magnetic nanoparticles to gene delivery
Abstract
Nanoparticle technology is being incorporated into many areas of molecular science and biomedicine. Because nanoparticles are small enough to enter almost all areas of the body, including the circulatory system and cells, they have been and continue to be exploited for basic biomedical research as well as clinical diagnostic and therapeutic applications. For example, nanoparticles hold great promise for enabling gene therapy to reach its full potential by facilitating targeted delivery of DNA into tissues and cells. Substantial progress has been made in binding DNA to nanoparticles and controlling the behavior of these complexes. In this article, we review research on binding DNAs to nanoparticles as well as our latest study on non-viral gene delivery using polyethylenimine-coated magnetic nanoparticles.
Keywords: Magnetofection; gene delivery; magnetic nanoparticles; polyethylenimine.
Figures
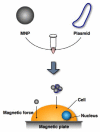

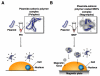
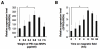
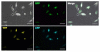
References
-
- Chouly C, Pouliquen D, Lucet I, Jeune JJ, Jallet P. Development of superparamagnetic nanoparticles for MRI: Effect of particle size, charge and surface nature on biodistribution. J. Microencapsul. 1996;13:245–255. - PubMed
-
- Yoo B, Pagel MD. An overview of responsive MRI contrast agents for molecular imaging. Front. Biosci. 2008;13:1733–1752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

