Neuromorphic silicon neuron circuits
- PMID: 21747754
- PMCID: PMC3130465
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2011.00073
Neuromorphic silicon neuron circuits
Abstract
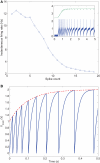
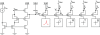
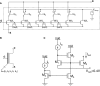
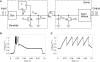
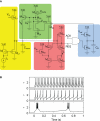
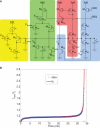
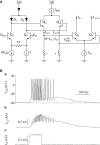
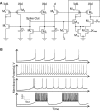
Hardware implementations of spiking neurons can be extremely useful for a large variety of applications, ranging from high-speed modeling of large-scale neural systems to real-time behaving systems, to bidirectional brain-machine interfaces. The specific circuit solutions used to implement silicon neurons depend on the application requirements. In this paper we describe the most common building blocks and techniques used to implement these circuits, and present an overview of a wide range of neuromorphic silicon neurons, which implement different computational models, ranging from biophysically realistic and conductance-based Hodgkin-Huxley models to bi-dimensional generalized adaptive integrate and fire models. We compare the different design methodologies used for each silicon neuron design described, and demonstrate their features with experimental results, measured from a wide range of fabricated VLSI chips.
Keywords: adaptive exponential; analog VLSI; circuit; conductance based; integrate and fire; log-domain; spiking; subthreshold.
Figures
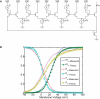
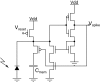
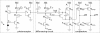
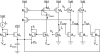
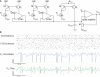
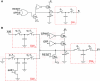
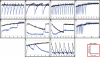
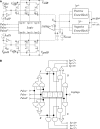

References
-
- Arthur J. V., Boahen K. (2004). Recurrently connected silicon neurons with active dendrites for one-shot learning. IEEE Int. Joint Conf. Neural Netw. 3, 1699–1704
-
- Azadmehr M., Abrahamsen J. P., Hafliger P. (2005). “A foveated AER imager chip,” in International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, ISCAS 2005, Vol. 3 (Kobe: IEEE; ), 2751–2754
-
- Bartolozzi C., Indiveri G. (2009). Global scaling of synaptic efficacy: homeostasis in silicon synapses. Neurocomputing 72, 726–731 10.1016/j.neucom.2008.05.016 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

