Diffusion-weighted MRI and quantitative biophysical modeling of hippocampal neurite loss in chronic stress
- PMID: 21747929
- PMCID: PMC3128590
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020653
Diffusion-weighted MRI and quantitative biophysical modeling of hippocampal neurite loss in chronic stress
Abstract
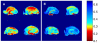
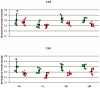
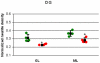
Chronic stress has detrimental effects on physiology, learning and memory and is involved in the development of anxiety and depressive disorders. Besides changes in synaptic formation and neurogenesis, chronic stress also induces dendritic remodeling in the hippocampus, amygdala and the prefrontal cortex. Investigations of dendritic remodeling during development and treatment of stress are currently limited by the invasive nature of histological and stereological methods. Here we show that high field diffusion-weighted MRI combined with quantitative biophysical modeling of the hippocampal dendritic loss in 21 day restraint stressed rats highly correlates with former histological findings. Our study strongly indicates that diffusion-weighted MRI is sensitive to regional dendritic loss and thus a promising candidate for non-invasive studies of dendritic plasticity in chronic stress and stress-related disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kim JJ, Diamond DM. The stressed hippocampus, synaptic plasticity and lost memories. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:453–462. - PubMed
-
- Roozendaal B, McEwen BS, Chattarji S. Stress, memory and the amygdala. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:423–433. - PubMed
-
- McEwen BS, Sapolsky RM. Stress and cognitive function. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995;5:205–216. - PubMed
-
- McEwen BS. Stress and hippocampal plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1999;22:105–122. - PubMed
-
- Xu L, Anwyl R, Rowan MJ. Behavioural stress facilitates the induction of long-term depression in the hippocampus. Nature. 1997;387:497–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

