From HIV Abandonment to Adoption: Case study of New Life Home for abandoned babies, Kenya
- PMID: 21748110
- PMCID: PMC3074889
From HIV Abandonment to Adoption: Case study of New Life Home for abandoned babies, Kenya
Abstract
Objective: The number of orphaned and vulnerable children (OVC) worldwide has increased as a result of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) pandemic. New Life Home (NLH) specialises in the care of infants who have been orphaned or abandoned, often because of their exposure to HIV and places them for adoption. This paper documents the lessons learnt from the Home's first 8.5 years of existence.
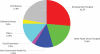
Methods: This retrospective study analyses the pattern of the 490 infants admitted at NLH. The characteristics of the infants' stay are analysed: bio-data, weight, HIV exposure, referring organisation/agent and outcome. This study ceased to follow infants after adoption, death, transferral to other homes, or reunion with own family. The infants came via health facilities (58%), local authorities (15%), good Samaritans (2%), and other children's homes (25%).
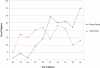
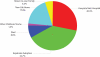
Results: At the end of the study period, 425 (92%) of babies were still alive. Of those who died, 80% were less than 6 months old (p<0.003) and 45% were HIV positive. A child mortality rate of 77.6/1000 was demonstrated with the key associated factors being HIV exposure (p <0001), and weight at admission (p=0.002). The mortality rate for the HIV exposed was 71/1000 at 6 months, 94.7/1000 at 12 months and 100.6/1000 at 18 months, while for those not exposed to the virus it was 43.3/1000 at 6 months and 46.7/1000 at 12 months. The major cause of death in the HIV exposed was pneumonia (56%) and septicaemia (22%). The majority of infants, 323 (67%) were adopted, some were reabsorbed into their biological families 31(6.3%) and a minority 7(1.4%) transferred to other children's homes which cater for older children.
Conclusion: NLH demonstrates a possible model of care for OVC as majority of vulnerable child can have the opportunity to be adopted and thereby a 'second lease' of life. This strategy is worth studying and duplicating in the mitigation of the OVC dilemma in HIV high prevalence countries in sub-Saharan Africa.
Keywords: AIDS; Care, orphans, Kenya; HIV.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Burden of Orphans and Vulnerable Children Due to HIV/AIDS in Cameroon.Open AIDS J. 2012;6:245-58. doi: 10.2174/1874613601206010245. Epub 2012 Oct 19. Open AIDS J. 2012. PMID: 23248738 Free PMC article.
-
Growth and development of abandoned babies in institutional care in Nairobi.East Afr Med J. 1999 Aug;76(8):430-5. East Afr Med J. 1999. PMID: 10520347
-
Understanding the association between caregiver sex and HIV infection among orphans and vulnerable children in Tanzania: learning from the USAID Kizazi Kipya project.BMC Health Serv Res. 2020 Apr 3;20(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s12913-020-05102-y. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020. PMID: 32245468 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Interventions for Orphans and Vulnerable Children Affected by HIV/AIDS Worldwide.Ann Behav Med. 2020 Nov 1;54(11):853-866. doi: 10.1093/abm/kaaa022. Ann Behav Med. 2020. PMID: 32525205 Free PMC article.
-
HIV Orphanhood Research and the Representation of Older Orphans in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Literature Review.J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2016 Jan-Feb;27(1):57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jana.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Sep 15. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2016. PMID: 26482073 Review.
Cited by
-
Profile of Perinatal Infections Among Abandoned Neonates Admitted in a Tertiary Hospital in Oman.Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2024 Nov;24(4):523-527. doi: 10.18295/squmj.11.2024.070. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2024. PMID: 39634798 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Republic of Kenya, Department of Children’s Services, Ministry of Home Affairs (MOHA) and National AIDS Control Council National Programme Guidelines on Orphans and Other Children Made Vulnerable by HIV/AIDS; Nairobi. 2003.
-
- Republic of Kenya, Ministry of Health, National AIDS and STD Control Programme . AIDS in Kenya: Background projections, impact, interventions and policy. 6th ed. Nairobi: NASCOP; 2001.
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS . Report on the Global HIV/AIDS Epidemic: 4th Report. UNAIDS; 2004. p. 65.
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS and United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) US Agency for International Development (USAID) Children on the Brink 2002: A joint report on orphan estimates and program strategies. Geneva: UNAIDS; 2002.
-
- UNAIDS . Report on the global HIV/AIDS Epidemic. UNAIDS; Jul, 2002.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources