Rheumatoid arthritis patients and rheumatologists approach the decision to escalate care differently: results of a maximum difference scaling experiment
- PMID: 21748861
- PMCID: PMC3698485
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.20551
Rheumatoid arthritis patients and rheumatologists approach the decision to escalate care differently: results of a maximum difference scaling experiment
Abstract
Objective: Antirheumatic treatment is frequently not appropriately modified, according to American College of Rheumatology guidelines, in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) as defined by a Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) score greater than 3.2. The objective of this study was to determine which factors most strongly influence patients' and rheumatologists' decisions to escalate care.
Methods: We administered a Maximum Difference Scaling survey to 106 rheumatologists and 213 patients with RA. The survey included 58 factors related to the decision to escalate care in RA. Participants answered 24 choice tasks. In each task, participants were asked to choose the most important factor from a set of 5. We used hierarchical Bayes modeling to generate the mean relative importance score (RIS) for each factor.
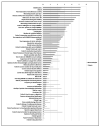
Results: For rheumatologists, the 5 most influential factors were number of swollen joints (mean ± SD RIS 5.2 ± 0.4), DAS28 score (mean ± SD RIS 5.2 ± 0.5), physician global assessment of disease activity (mean ± SD RIS 5.2 ± 0.6), worsening erosions over the last year (mean ± SD RIS 5.2 ± 0.5), and RA disease activity now compared to 3 months ago (mean ± SD RIS 5.1 ± 0.6). For patients, the 5 most important factors were current level of physical functioning (mean ± SD RIS 4.3 ± 1.1), motivation to get better (mean ± SD RIS 3.5 ± 1.4), trust in their rheumatologist (mean ± SD RIS 3.5 ± 1.6), satisfaction with current disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (mean ± SD RIS 3.4 ± 1.4), and current number of painful joints (mean ± SD RIS 3.4 ± 1.4).
Conclusion: Factors influencing the decision to escalate care differ between rheumatologists and patients. Better communication between patients and their physicians may improve treatment planning in RA patients with active disease.
Copyright © 2011 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Allaart CF, van Zeben D, Kerstens PJ, Hazes JM, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of four different treatment strategies in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (the BeSt study): a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(11):3381–90. - PubMed
-
- Grigor C, Capell H, Stirling A, McMahon AD, Lock P, Vallance R, et al. Effect of a treatment strategy of tight control for rheumatoid arthritis (the TICORA study): a single-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2004;364(9430):263–9. - PubMed
-
- Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Kerstens PJ, Nielen MM, Vos K, van Schaardenburg D, et al. DAS-driven therapy versus routine care in patients with recent-onset active rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(1):65–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical