Algal Functional Annotation Tool: a web-based analysis suite to functionally interpret large gene lists using integrated annotation and expression data
- PMID: 21749710
- PMCID: PMC3144025
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-282
Algal Functional Annotation Tool: a web-based analysis suite to functionally interpret large gene lists using integrated annotation and expression data
Abstract
Background: Progress in genome sequencing is proceeding at an exponential pace, and several new algal genomes are becoming available every year. One of the challenges facing the community is the association of protein sequences encoded in the genomes with biological function. While most genome assembly projects generate annotations for predicted protein sequences, they are usually limited and integrate functional terms from a limited number of databases. Another challenge is the use of annotations to interpret large lists of 'interesting' genes generated by genome-scale datasets. Previously, these gene lists had to be analyzed across several independent biological databases, often on a gene-by-gene basis. In contrast, several annotation databases, such as DAVID, integrate data from multiple functional databases and reveal underlying biological themes of large gene lists. While several such databases have been constructed for animals, none is currently available for the study of algae. Due to renewed interest in algae as potential sources of biofuels and the emergence of multiple algal genome sequences, a significant need has arisen for such a database to process the growing compendiums of algal genomic data.
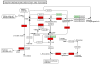
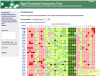
Description: The Algal Functional Annotation Tool is a web-based comprehensive analysis suite integrating annotation data from several pathway, ontology, and protein family databases. The current version provides annotation for the model alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, and in the future will include additional genomes. The site allows users to interpret large gene lists by identifying associated functional terms, and their enrichment. Additionally, expression data for several experimental conditions were compiled and analyzed to provide an expression-based enrichment search. A tool to search for functionally-related genes based on gene expression across these conditions is also provided. Other features include dynamic visualization of genes on KEGG pathway maps and batch gene identifier conversion.
Conclusions: The Algal Functional Annotation Tool aims to provide an integrated data-mining environment for algal genomics by combining data from multiple annotation databases into a centralized tool. This site is designed to expedite the process of functional annotation and the interpretation of gene lists, such as those derived from high-throughput RNA-seq experiments. The tool is publicly available at http://pathways.mcdb.ucla.edu.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W169-75. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm415. Epub 2007 Jun 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17576678 Free PMC article.
-
An Experimental Approach to Genome Annotation: This report is based on a colloquium sponsored by the American Academy of Microbiology held July 19-20, 2004, in Washington, DC.Washington (DC): American Society for Microbiology; 2004. Washington (DC): American Society for Microbiology; 2004. PMID: 33001599 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Visual annotation display (VLAD): a tool for finding functional themes in lists of genes.Mamm Genome. 2015 Oct;26(9-10):567-73. doi: 10.1007/s00335-015-9570-2. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Mamm Genome. 2015. PMID: 26047590 Free PMC article.
-
DAVID Knowledgebase: a gene-centered database integrating heterogeneous gene annotation resources to facilitate high-throughput gene functional analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Nov 2;8:426. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-426. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17980028 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Disease Sequence Data Resource (MSeqDR): a global grass-roots consortium to facilitate deposition, curation, annotation, and integrated analysis of genomic data for the mitochondrial disease clinical and research communities.Mol Genet Metab. 2015 Mar;114(3):388-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.11.016. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Mol Genet Metab. 2015. PMID: 25542617 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Copper response regulator1-dependent and -independent responses of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii transcriptome to dark anoxia.Plant Cell. 2013 Sep;25(9):3186-211. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.115741. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 24014546 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular toxicity pathways of inorganic and methyl mercury in the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 14;7(1):8034. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08515-8. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28808314 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional Depletion of the Chlamydomonas Chloroplast ClpP Protease Activates Nuclear Genes Involved in Autophagy and Plastid Protein Quality Control.Plant Cell. 2014 May;26(5):2201-2222. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.124842. Epub 2014 May 30. Plant Cell. 2014. PMID: 24879428 Free PMC article.
-
System-level network analysis of nitrogen starvation and recovery in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii reveals potential new targets for increased lipid accumulation.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2014 Dec 24;7:171. doi: 10.1186/s13068-014-0171-1. eCollection 2014. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2014. PMID: 25663847 Free PMC article.
-
Stress responses of the oil-producing green microalga Botryococcus braunii Race B.PeerJ. 2016 Dec 6;4:e2748. doi: 10.7717/peerj.2748. eCollection 2016. PeerJ. 2016. PMID: 27957393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):44–57. - PubMed
-
- Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA), Ingenuity Systems. http://www.ingenuity.com

