Effect of oral care gel on the quality of life for oral lichen planus in patients with chronic HCV infection
- PMID: 21749712
- PMCID: PMC3149004
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-348
Effect of oral care gel on the quality of life for oral lichen planus in patients with chronic HCV infection
Abstract
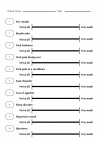
Background: Oral lichen planus (OLP) decreases the quality of life because it can cause spontaneous pain during eating and tooth-brushing and an uncomfortable feeling in the mouth. In addition, OLP may be associated with HCV-related liver disease.We investigated the visual analogue scale (VAS) and effects of oral care gel, REFRECARE-H®, on patients with OLP associated with HCV infection.
Results: Nine OLP patients (mean age 67.9 ± 7.6 years) with HCV-related liver diseases were recruited and their VAS score determined along with a biochemical examination of the blood. Types of OLP included erosive (6 patients) and reticular (3). REFRECARE-H®, an oral care gel (therapeutic dentifrice) containing hinokitiol, was applied by each patient as a thin layer on the oral membrane, after each meal and at bedtime for 30 days. Application of REFRECARE-H® improved the quality of life in all terms of dry mouth, breath odor, oral freshness, oral pain during rest, oral pain at a mealtimes, taste disorder, loss of appetite, sleep disorder, depressive mood and jitteriness. VAS scores of dry mouth, breath odor, oral freshness, and sleep disorder were significantly increased 30 days after application of REFRECARE-H® (P = 0.01, P = 0.05, P = 0.03, P = 0.04). VAS scores of oral pain at a mealtimes and taste disorder were increased 30 days after application of REFRECARE-H® (P = 0.06). There was an absence of side effects.
Conclusions: REFRECARE-H® improved the quality of life for OLP. It is necessary for the hepatologist to educate patients regarding oral hygiene, as well as provide treatment of liver disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Oral Care Gel for Burning Mouth Syndrome in a Patient with Hepatitis C: A Case Report.Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug 17;11(2):480-487. doi: 10.1159/000479495. eCollection 2017 May-Aug. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 29033766 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical impact of direct-acting antiviral treatment on patients affected by hepatitis C virus-related oral lichen planus: a cohort study.Clin Oral Investig. 2022 Aug;26(8):5409-5417. doi: 10.1007/s00784-022-04507-9. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Clin Oral Investig. 2022. PMID: 35477818 Free PMC article.
-
MANAGEMENT OF EROSIVE ORAL LICHEN PLANUS ASSOCIATED WITH CHRONIC HEPATITIS C.J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2024 Jul-Sep;36(3):651-656. doi: 10.55519/JAMC-03-12370. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2024. PMID: 39623851
-
Pathophysiology, etiologic factors, and clinical management of oral lichen planus, part I: facts and controversies.Clin Dermatol. 2010 Jan-Feb;28(1):100-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2009.03.004. Clin Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20082959 Review.
-
Steriods in the treatment of lichen planus: a review.J Oral Sci. 2008 Dec;50(4):377-85. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.50.377. J Oral Sci. 2008. PMID: 19106464 Review.
Cited by
-
Candidiasis and other oral mucosal lesions during and after interferon therapy for HCV-related chronic liver diseases.BMC Gastroenterol. 2012 Nov 2;12:155. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-12-155. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23122361 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Oral Care in a Patient with Depression and Burning Mouth Syndrome during the COVID-19 Pandemic.Case Rep Dent. 2021 Oct 26;2021:3039269. doi: 10.1155/2021/3039269. eCollection 2021. Case Rep Dent. 2021. PMID: 34712498 Free PMC article.
-
Antiproliferative Activity of Hinokitiol, a Tropolone Derivative, Is Mediated via the Inductions of p-JNK and p-PLCγ1 Signaling in PDGF-BB-Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.Molecules. 2015 May 7;20(5):8198-212. doi: 10.3390/molecules20058198. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25961161 Free PMC article.
-
The superiority trial of Baduanjin training on patients chronic low back pain: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Nov 6;24(1):383. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04649-1. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 39506781 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation physical characteristics and comparison antimicrobial and anti-inflammation potentials of dental root canal sealers containing hinokitiol in vitro.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 10;9(6):e94941. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094941. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24915566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Higuchi M, Tanaka E, Kiyosawa K. Epidemiology and clinical aspects on hepatitis C. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2002;55:69–77. - PubMed
-
- Gumber SC, Chopra S. Hepatitis C: a multifaceted disease. Review of extrahepatic manifestations. Ann Intern Med. 1995;123:615–620. - PubMed
-
- Rebora A. Skin diseases associated with hepatitis C virus: Facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2010;28:489–496. - PubMed
-
- Loustaud-Ratti V, Riche A, Liozon E, Labrousse F, Soria P, Rogez S, Babany G, Delaire L, Denis F, Vidal E. Prevalence and characteristics of Sjögren's syndrome or Sicca syndrome in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a prospective study. J Rheumatol. 2001;28:2245–2251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical