Analysis of mammalian sphingolipids by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and tissue imaging mass spectrometry (TIMS)
- PMID: 21749933
- PMCID: PMC3205276
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.06.027
Analysis of mammalian sphingolipids by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and tissue imaging mass spectrometry (TIMS)
Abstract
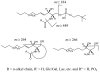
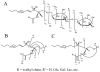
Sphingolipids are a highly diverse category of molecules that serve not only as components of biological structures but also as regulators of numerous cell functions. Because so many of the structural features of sphingolipids give rise to their biological activity, there is a need for comprehensive or "sphingolipidomic" methods for identification and quantitation of as many individual subspecies as possible. This review defines sphingolipids as a class, briefly discusses classical methods for their analysis, and focuses primarily on liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and tissue imaging mass spectrometry (TIMS). Recently, a set of evolving and expanding methods have been developed and rigorously validated for the extraction, identification, separation, and quantitation of sphingolipids by LC-MS/MS. Quantitation of these biomolecules is made possible via the use of an internal standard cocktail. The compounds that can be readily analyzed are free long-chain (sphingoid) bases, sphingoid base 1-phosphates, and more complex species such as ceramides, ceramide 1-phosphates, sphingomyelins, mono- and di-hexosylceramides, sulfatides, and novel compounds such as the 1-deoxy- and 1-(deoxymethyl)-sphingoid bases and their N-acyl-derivatives. These methods can be altered slightly to separate and quantitate isomeric species such as glucosyl/galactosylceramide. Because these techniques require the extraction of sphingolipids from their native environment, any information regarding their localization in histological slices is lost. Therefore, this review also describes methods for TIMS. This technique has been shown to be a powerful tool to determine the localization of individual molecular species of sphingolipids directly from tissue slices.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Merrill AH, Jr., Wang MD, Park M, Sullards MC. (Glyco)sphingolipidology: an amazing challenge and opportunity for systems biology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007;32:457–468. - PubMed
-
- Sullards MC, Allegood JC, Kelly S, Wang E, Haynes CA, Park H, Chen Y, Merrill AH., Jr. Structure-specific, quantitative methods for analysis of sphingolipids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: “inside-out” sphingolipidomics. Methods Enzymol. 2007;432:83–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

