Is high dose therapy superior to conventional dose therapy as initial treatment for relapsed germ cell tumors? The TIGER Trial
- PMID: 21750688
- PMCID: PMC3133961
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.2.374
Is high dose therapy superior to conventional dose therapy as initial treatment for relapsed germ cell tumors? The TIGER Trial
Abstract
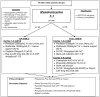
Metastatic germ cell tumours (GCTs) are usually cured with cisplatin based chemotherapy and standard treatment algorithms are established. However when this treatment fails and the disease relapses, standard treatment is much more uncertain. Both conventional dose therapy (CDT) and high dose therapy (HDT) are widely used, due to the lack of conclusive data supporting one specific approach. A recent retrospective analysis focusing on this population suggested a significant benefit for HDT. Retrospective analyses are prone to bias, and therefore while this data is provocative it is by no mean conclusive. For this reason the international community is supporting a prospective randomised trial in this area comparing CDT(TIP) with sequential HDT (TICE). The planned open labelled randomised phase III study (TIGER) is due to open in 2011 and will recruit 390 patients to detect a 13% difference in 2 year progression free survival (primary endpoint). It is hoped that this large study will conclusively resolve the uncertainty which currently exists.
Keywords: Metastatic germ cell tumours; dose therapy; relapses.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Average Years of Life Lost Per Person Dying of Cancer, All Races, Both Sexes, 2004; SEER DATABASE 1975-2004. NIH; http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2004/results_figure/sect_01_zfig.19.pdf.
-
- Lorch A, Kollmannsberger C, Hartmann JT. et al. Single versus sequential high-dose chemotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory germ cell tumors: a prospective randomized multicenter trial of the German Testicular Cancer Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2007 Jul 1;25(19):2778–84. - PubMed
-
- Daugaard G. Management of poor-prognosis or relapsed germ-cell cancer. BJU Int. 2009 Nov;104:1392–7. - PubMed
-
- Connolly RM, McCaffrey JA. High-dose chemotherapy plus stem cell transplantation in advanced germ cell cancer: a review. Eur Urol. 2009 Jul;56(1):57–64. - PubMed
-
- Kondagunta GV, Bacik J, Donadio A, Bajorin D, Marion S, Sheinfeld J, Bosl GJ, Motzer RJ. Combination of paclitaxel, ifosfamide, and cisplatin is an effective second-line therapy for patients with relapsed testicular germ cell tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2005 Sep 20;23(27):6549–55. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources