Rapid improvement of glycemic control in type 2 diabetes using weekly intensive multifactorial interventions: structured glucose monitoring, patient education, and adjustment of therapy-a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 21751888
- PMCID: PMC3182678
- DOI: 10.1089/dia.2011.0054
Rapid improvement of glycemic control in type 2 diabetes using weekly intensive multifactorial interventions: structured glucose monitoring, patient education, and adjustment of therapy-a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: We evaluated intensive intervention in poorly controlled patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus involving weekly clinic visits and adjustment of therapy with analysis of three seven-point glucose profiles and intervention from an interdisciplinary staff.
Methods: Sixty-three patients were randomized to an intensive treatment group that obtained self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) profiles (six or seven values per day, 3 days/week) and were seen in the clinic at Weeks 1-6 and 12. SMBG results were downloaded, analyzed using Accu-Chek(®) 360° software (Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, IN), and used to adjust therapy. Control group subjects obtained glucose profiles and had clinic visits only at Weeks 0, 6, and 12.
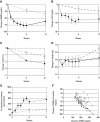
Results: There were highly statistically significant improvements in the intensive treatment group compared with the control group between Weeks 0 and 6 with greater reductions in weekly mean glycemia (WMG) (-76.7±8.9 mg/dL vs. -20.5±8.1 mg/dL), glycemic variability (SD) (-16.3±3.1 mg/dL vs. -5.0±3.1 mg/dL), and glycated hemoglobin (-1.82±0.16% vs. -0.66±0.22%) without significant changes in frequency of hypoglycemia or weight. Improvements were sustained in the intensive treatment group through Week 12. A minimal but statistically significant degree of improvement was seen in the control group at Week 12.
Conclusions: This short-term pilot study of an intensive monitoring, educational, and pharmacological interventions program resulted in dramatic improvement of glycemic control within 6 weeks, and these effects are sustained through Week 12. SMBG glucose profiles, calculation of WMG and SD, and graphical displays of glucose data can improve the effectiveness of adjustment of therapy at weekly clinic visits when combined with intensive support from a multidisciplinary team.
Figures
References
-
- Gæde P. Vedel P. Larsen N. Jensen GVH. Parving HH. Pedersen O. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:383–393. - PubMed
-
- Ziemer DC. Miller CD. Rhee M. Doyle JP. Watkins C., Jr Cook CB. Gallina DL. El-Kebbi IM. Barnes CS. Dunbar VG. Branch WT., Jr Phillips LS. Clinical inertia contributes to poor diabetes control in a primary care setting. Diabetes Educ. 2005;31:564–571. - PubMed
-
- Dailey G. Assessing glycemic control with self-monitoring of blood glucose and hemoglobin A1c measurements. Mayo Clin Proc. 2007;82:229–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
