Outcomes of patients undergoing early sepsis resuscitation for cryptic shock compared with overt shock
- PMID: 21752522
- PMCID: PMC3179778
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2011.06.015
Outcomes of patients undergoing early sepsis resuscitation for cryptic shock compared with overt shock
Abstract
Introduction: We sought to compare the outcomes of patients with cryptic versus overt shock treated with an emergency department (ED) based early sepsis resuscitation protocol.
Methods: Pre-planned secondary analysis of a large, multicenter ED-based randomized controlled trial of early sepsis resuscitation. All subjects were treated with a quantitative resuscitation protocol in the ED targeting 3 physiological variables: central venous pressure, mean arterial pressure and either central venous oxygen saturation or lactate clearance. The study protocol was continued until all endpoints were achieved or a maximum of 6h. Outcomes data of patients who were enrolled with a lactate ≥ 4mmol/L and normotension (cryptic shock) were compared to those enrolled with sustained hypotension after fluid challenge (overt shock). The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality.
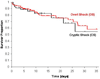
Results: A total of 300 subjects were enrolled, 53 in the cryptic shock group and 247 in the overt shock group. The demographics and baseline characteristics were similar between the groups. The primary endpoint of in-hospital mortality was observed in 11/53 (20%, 95% CI 11-34) in the cryptic shock group and 48/247 (19%, 95% CI 15-25) in the overt shock group, difference of 1% (95% CI -10 to 14; log rank test p=0.81).
Conclusion: Severe sepsis with cryptic shock carries a mortality rate not significantly different from that of overt septic shock. These data suggest the need for early aggressive screening for and treatment of patients with an elevated serum lactate in the absence of hypotension.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflicts of interests to report.
Figures
Comment in
-
Early goal-directed therapy in the emergency department - lactate is biomarker of illness severity, but of which disease process?Resuscitation. 2011 Oct;82(10):1263-4. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2011.06.019. Epub 2011 Jun 24. Resuscitation. 2011. PMID: 21752523 No abstract available.
References
-
- Angus D, Linde-Zwirble W, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky M. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Dombrovskiy VY, Martin AA, Sunderram J, Paz HL. Rapid increase in hospitalization and mortality rates for severe sepsis in the United States: A trend analysis from 1993 to 2003. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:1244–1250. - PubMed
-
- Wang HE, Shapiro NI, Angus DC, Yealy DM. National estimates of severe sepsis in United States emergency departments. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:1928–1936. - PubMed
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:296–327. - PubMed
-
- Donnino MW, Nguyen B, Jacobsen G, Tomianovich M, Rivers E. Cryptic septic shock: a sub-analysis of early, goal-directed therapy. Chest. 2003;124 90S-90b.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources