Long-term trends in hip arthroplasty use and volume
- PMID: 21752578
- PMCID: PMC3193900
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arth.2011.04.043
Long-term trends in hip arthroplasty use and volume
Abstract
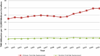
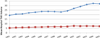
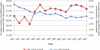
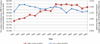
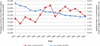
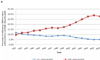
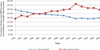
We used Medicare administrative data to examine trends in primary and revision total hip arthroplasty (THA) use and hospital volume. Between 1991 and 2005, primary and revision THA use increased by 40.9% and 16.8%, respectively. The percentage of primary THA procedures performed in high-volume hospitals (those in the highest quintile of volume) increased slightly from 58.0% of all procedures in 1991 to 58.7% in 2005 (P < .01). The percentage of revisions performed in high-volume hospitals increased from 60.9% to 62.4% (P < .01). The percentage of primary THA procedures performed by low-volume hospitals remained relatively stable (P = .36), whereas the percentage of revision THA performed by low-volume hospitals declined (P < .001). In aggregate, these results suggest minimal evidence that regionalization of THA is occurring.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the Department of Veterans Affairs. The funding sources had no role in the analyses or drafting of this manuscript. None of the authors have any conflicts of interest. Dr. Cram has received consulting fees from The Consumers Union (publisher of Consumer Reports Magazine) and Vanguard Health Inc. for work advice on quality improvement initiatives. Dr. Callaghan is the President of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgery and has served as a consultant to several orthopaedic implant manufacturers.
Figures



References
-
- Lohmander LS, Engesaeter LB, Herberts P, Ingvarsson T, Lucht U, Puolakka TJ. Standardized incidence rates of total hip replacement for primary hip osteoarthritis in the 5 Nordic countries: similarities and differences. Acta Orthop. 2006 Oct;77(5):733–740. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Health, United States, 2009. U.S. Centers for Disease Control; 2009.
-
- Khatod M, Inacio M, Paxton EW, et al. Knee replacement: epidemiology, outcomes, and trends in Southern California: 17,080 replacements from 1995 through 2004. Acta Orthop. 2008 Dec;79(6):812–819. - PubMed
-
- Katz JN, Phillips CB, Baron JA, et al. Association of hospital and surgeon volume of total hip replacement with functional status and satisfaction three years following surgery. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 2003 Feb;48(2):560–568. [see comment] - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

