The L-coding region of the DA strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus causes dysfunction and death of myelin-synthesizing cells
- PMID: 21752920
- PMCID: PMC3165738
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00178-11
The L-coding region of the DA strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus causes dysfunction and death of myelin-synthesizing cells
Abstract
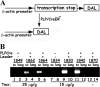
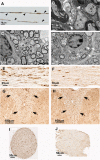
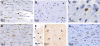
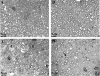
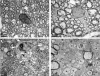
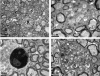
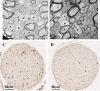
The DA strain and other members of the TO subgroup of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV) induce an early transient subclinical neuronal disease followed by a chronic progressive inflammatory demyelination, with persistence of the virus in the central nervous system (CNS) for the life of the mouse. Although TMEV-induced demyelinating disease (TMEV-IDD) is thought to be immune mediated, there is also evidence that supports a role for the virus in directly inducing demyelination. In order to clarify the function of DA virus genes, we generated a transgenic mouse that had tamoxifen-inducible expression of the DA L-coding region in oligodendrocytes (and Schwann cells), a cell type in which the virus is known to persist. Tamoxifen-treated young transgenic mice usually developed an acute progressive fatal paralysis, with abnormalities of the oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells and demyelination, but without significant lymphocytic infiltration; later treatment led to transient weakness with demyelination and persistent expression of the recombined transgene. These findings demonstrate that a high level of expression of DA L can cause the death of myelin-synthesizing cells and death of the mouse, while a lower level of L expression (which can persist) can lead to cellular dysfunction with survival. The results suggest that expression of DA L plays an important role in the pathogenesis of TMEV-IDD. Virus-induced infection and death of oligodendrocytes may play a part in the demyelination of other diseases in which an immune-mediated mechanism has been stressed, including multiple sclerosis.
Figures
References
-
- Brahic M. 2010. Multiple sclerosis and viruses. Ann. Neurol. 68:6–8 - PubMed
-
- Carlson N. G., Hill K. E., Tsunoda I., Fujinami R. S., Rose J. W. 2006. The pathologic role for COX-2 in apoptotic oligodendrocytes in virus induced demyelinating disease: implications for multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol 174:21–31 - PubMed
-
- Chen H. H., Kong W. P., Zhang L., Ward P. L., Roos R. P. 1995. A picornaviral protein synthesized out of frame with the polyprotein plays a key role in a virus-induced immune-mediated demyelinating disease. Nat. Med. 1:927–931 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

