The regenerative capacity of zebrafish reverses cardiac failure caused by genetic cardiomyocyte depletion
- PMID: 21752928
- PMCID: PMC3143562
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.068601
The regenerative capacity of zebrafish reverses cardiac failure caused by genetic cardiomyocyte depletion
Abstract
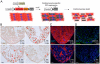
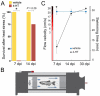
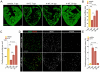
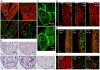
Natural models of heart regeneration in lower vertebrates such as zebrafish are based on invasive surgeries causing mechanical injuries that are limited in size. Here, we created a genetic cell ablation model in zebrafish that facilitates inducible destruction of a high percentage of cardiomyocytes. Cell-specific depletion of over 60% of the ventricular myocardium triggered signs of cardiac failure that were not observed after partial ventricular resection, including reduced animal exercise tolerance and sudden death in the setting of stressors. Massive myocardial loss activated robust cellular and molecular responses by endocardial, immune, epicardial and vascular cells. Destroyed cardiomyocytes fully regenerated within several days, restoring cardiac anatomy, physiology and performance. Regenerated muscle originated from spared cardiomyocytes that acquired ultrastructural and electrophysiological characteristics of de-differentiation and underwent vigorous proliferation. Our study indicates that genetic depletion of cardiomyocytes, even at levels so extreme as to elicit signs of cardiac failure, can be reversed by natural regenerative capacity in lower vertebrates such as zebrafish.
Figures


References
-
- Akazawa H., Komazaki S., Shimomura H., Terasaki F., Zou Y., Takano H., Nagai T., Komuro I. (2004). Diphtheria toxin-induced autophagic cardiomyocyte death plays a pathogenic role in mouse model of heart failure. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 41095-41103 - PubMed
-
- Beltrami A. P., Barlucchi L., Torella D., Baker M., Limana F., Chimenti S., Kasahara H., Rota M., Musso E., Urbanek K., et al. (2003). Adult cardiac stem cells are multipotent and support myocardial regeneration. Cell 114, 763-776 - PubMed
-
- Beltrami C. A., Finato N., Rocco M., Feruglio G. A., Puricelli C., Cigola E., Quaini F., Sonnenblick E. H., Olivetti G., Anversa P. (1994). Structural basis of end-stage failure in ischemic cardiomyopathy in humans. Circulation 89, 151-163 - PubMed
-
- Bersell K., Arab S., Haring B., Kuhn B. (2009). Neuregulin1/ErbB4 signaling induces cardiomyocyte proliferation and repair of heart injury. Cell 138, 257-270 - PubMed
-
- Braunwald E., Bonow R. O. (2010). Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. Philadelphia: Saunders;
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

