A late phase of germ plasm accumulation during Drosophila oogenesis requires lost and rumpelstiltskin
- PMID: 21752933
- PMCID: PMC3143563
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.065029
A late phase of germ plasm accumulation during Drosophila oogenesis requires lost and rumpelstiltskin
Abstract
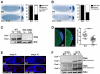
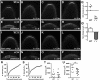
Asymmetric mRNA localization is an effective mechanism for establishing cellular and developmental polarity. Posterior localization of oskar in the Drosophila oocyte targets the synthesis of Oskar to the posterior, where Oskar initiates the assembly of the germ plasm. In addition to harboring germline determinants, the germ plasm is required for localization and translation of the abdominal determinant nanos. Consequently, failure of oskar localization during oogenesis results in embryos lacking germ cells and abdominal segments. oskar accumulates at the oocyte posterior during mid-oogenesis through a well-studied process involving kinesin-mediated transport. Through live imaging of oskar mRNA, we have uncovered a second, mechanistically distinct phase of oskar localization that occurs during late oogenesis and results in amplification of the germ plasm. Analysis of two newly identified oskar localization factors, Rumpelstiltskin and Lost, that are required specifically for this late phase of oskar localization shows that germ plasm amplification ensures robust abdomen and germ cell formation during embryogenesis. In addition, our results indicate the importance of mechanisms for adapting mRNAs to utilize multiple localization pathways as necessitated by the dramatic changes in ovarian physiology that occur during oogenesis.
Figures




References
-
- Anguera M. C., Suh J. R., Ghandour H., Nasrallah I. M., Selhub J., Stover P. J. (2003). Methenyltetrahydrofolate synthetase regulates folate turnover and accumulation. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 29856-29862 - PubMed
-
- Bergsten S. E., Gavis E. R. (1999). Role for mRNA localization in translational activation but not spatial restriction of nanos RNA. Development 126, 659-669 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

