Physical activity attenuates the effect of low birth weight on insulin resistance in adolescents: findings from two observational studies
- PMID: 21752955
- PMCID: PMC3161315
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-1670
Physical activity attenuates the effect of low birth weight on insulin resistance in adolescents: findings from two observational studies
Abstract
Objective: To examine whether physical activity influences the association between birth weight and insulin resistance in adolescents.
Research design and methods: The study comprised adolescents who participated in two cross-sectional studies: the Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence (HELENA) study (n = 520, mean age = 14.6 years) and the Swedish part of the European Youth Heart Study (EYHS) (n = 269, mean age = 15.6 years). Participants had valid data on birth weight (parental recall), BMI, sexual maturation, maternal education, breastfeeding, physical activity (accelerometry, counts/minute), fasting glucose, and insulin. Insulin resistance was assessed by homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). Maternal education level and breastfeeding duration were reported by the mothers.
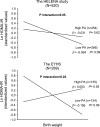
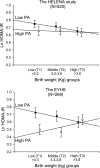
Results: There was a significant interaction of physical activity in the association between birth weight and HOMA-IR (logarithmically transformed) in both the HELENA study and the EYHS (P = 0.05 and P = 0.03, respectively), after adjusting for sex, age, sexual maturation, BMI, maternal education level, and breastfeeding duration. Stratified analyses by physical activity levels (below/above median) showed a borderline inverse association between birth weight and HOMA-IR in the low-active group (standardized β = -0.094, P = 0.09, and standardized β = -0.156, P = 0.06, for HELENA and EYHS, respectively), whereas no evidence of association was found in the high-active group (standardized β = -0.031, P = 0.62, and standardized β = 0.053, P = 0.55, for HELENA and EYHS, respectively).
Conclusions: Higher levels of physical activity may attenuate the adverse effects of low birth weight on insulin sensitivity in adolescents. More observational data, from larger and more powerful studies, are required to test these findings.
Figures
References
-
- Lawlor DA, Riddoch CJ, Page AS, et al. The association of birthweight and contemporary size with insulin resistance among children from Estonia and Denmark: findings from the European Youth Heart Study. Diabet Med 2005;22:921–930 - PubMed
-
- Whincup PH, Kaye SJ, Owen CG, et al. Birth weight and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. JAMA 2008;300:2886–2897 - PubMed
-
- Ludwig DS, Ebbeling CB. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in children: primary care and public health considerations. JAMA 2001;286:1427–1430 - PubMed
-
- Rizzo NS, Ruiz JR, Oja L, Veidebaum T, Sjöström M. Associations between physical activity, body fat, and insulin resistance (homeostasis model assessment) in adolescents: the European Youth Heart Study. Am J Clin Nutr 2008;87:586–592 - PubMed

