Phoenix 100 versus Vitek 2 in the identification of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria: a comprehensive meta-analysis
- PMID: 21752980
- PMCID: PMC3165577
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00182-11
Phoenix 100 versus Vitek 2 in the identification of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria: a comprehensive meta-analysis
Abstract
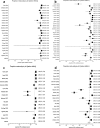
Phoenix 100 and Vitek 2 (operating with the current colorimetric cards) are commonly used in hospital laboratories for rapid identification of microorganisms. The present meta-analysis aims to evaluate and compare their performance on Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The MEDLINE database was searched up to October 2010 for the retrieval of relevant articles. Pooled correct identification rates were derived from random-effects models, using the arcsine transformation. Separate analyses were conducted at the genus and species levels; subanalyses and meta-regression were undertaken to reveal meaningful system- and study-related modifiers. A total of 29 (6,635 isolates) and 19 (4,363 isolates) articles were eligible for Phoenix and colorimetric Vitek 2, respectively. No significant differences were observed between Phoenix and Vitek 2 either at the genus (97.70% versus 97.59%, P = 0.919) or the species (92.51% versus 88.77%, P = 0.149) level. Studies conducted with conventional comparator methods tended to report significantly better results compared to those using molecular reference techniques. Speciation of Staphylococcus aureus was significantly more accurate in comparison to coagulase-negative staphylococci by both Phoenix (99.78% versus 88.42%, P < 0.00001) and Vitek 2 (98.22% versus 91.89%, P = 0.043). Vitek 2 also reached higher correct identification rates for Gram-negative fermenters versus nonfermenters at the genus (99.60% versus 95.90%, P = 0.004) and the species (97.42% versus 84.85%, P = 0.003) level. In conclusion, the accuracy of both systems seems modified by underlying sample- and comparator method-related parameters. Future simultaneous assessment of the instruments against molecular comparator procedures may facilitate interpretation of the current observations.
Figures
Comment in
-
Phoenix® Vitek® in bacterial identification.Rev Chilena Infectol. 2012 Feb;29(1):118. doi: 10.4067/S0716-10182012000100021. Rev Chilena Infectol. 2012. PMID: 23650650 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Fast and reliable bacterial identification direct from positive blood culture using a new TFA sample preparation protocol and the Vitek® MS system.J Microbiol Methods. 2015 Feb;109:157-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2014.12.009. Epub 2014 Dec 22. J Microbiol Methods. 2015. PMID: 25541363
-
Comparative evaluation of the Vitek-2 Compact and Phoenix systems for rapid identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing directly from blood cultures of Gram-negative and Gram-positive isolates.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012 Jan;72(1):20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2011.09.015. Epub 2011 Oct 24. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22030102
-
Use of the MicroSeq 500 16S rRNA gene-based sequencing for identification of bacterial isolates that commercial automated systems failed to identify correctly.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43(2):615-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.2.615-619.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15695654 Free PMC article.
-
Culture-negative surgical site infections.Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2006 Dec;7(6):555-65. doi: 10.1089/sur.2006.7.555. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2006. PMID: 17233574 Review.
-
Genetic systems for studying obligate intracellular pathogens: an update.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014 Feb;17:11-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2013.10.006. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24581687 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multicenter evaluation of the Vitek MS matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry system for identification of Gram-positive aerobic bacteria.J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Jul;51(7):2225-31. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00682-13. Epub 2013 May 8. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23658261 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of the matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry system for rapid identification of streptococci: a review.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2017 Jun;36(6):1005-1012. doi: 10.1007/s10096-016-2879-2. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28116553
-
Development of rapid phenotypic system for the identification of Gram-negative oxidase-positive bacilli in resource-limited settings.J Biosci. 2013 Jun;38(2):329-37. doi: 10.1007/s12038-013-9317-8. J Biosci. 2013. PMID: 23660668
-
Comparison of the epidemiological behavior of mastitis pathogens by applying time-series analysis in results of milk samples submitted for microbiological examination.Vet Res Commun. 2013 Dec;37(4):259-67. doi: 10.1007/s11259-013-9570-1. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Vet Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23779256
-
Identification of Rare Bacterial Pathogens by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and MALDI-TOF MS.J Vis Exp. 2016 Jul 11;(113):53176. doi: 10.3791/53176. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 27500532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abele-Horn M., Stoy K., Frosch M., Reinert R. R. 2006. Comparative evaluation of a new Vitek 2 system for identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 25: 55–57 - PubMed
-
- Dickinson Becton. 2005. BD Phoenix system user's manual, document L003342(M). Becton Dickinson and Company, Sparks, MD
-
- Begg C. B., Mazumdar M. 1994. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50: 1088–1101 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

