Growth arrest by trehalose-6-phosphate: an astonishing case of primary metabolite control over growth by way of the SnRK1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 21753116
- PMCID: PMC3165867
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.111.180422
Growth arrest by trehalose-6-phosphate: an astonishing case of primary metabolite control over growth by way of the SnRK1 signaling pathway
Abstract
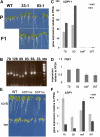
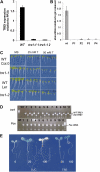
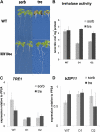
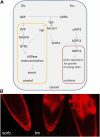
The strong regulation of plant carbon allocation and growth by trehalose metabolism is important for our understanding of the mechanisms that determine growth and yield, with obvious applications in crop improvement. To gain further insight on the growth arrest by trehalose feeding, we first established that starch-deficient seedlings of the plastidic phosphoglucomutase1 mutant were similarly affected as the wild type on trehalose. Starch accumulation in the source cotyledons, therefore, did not cause starvation and consequent growth arrest in the growing zones. We then screened the FOX collection of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) expressing full-length cDNAs for seedling resistance to 100 mm trehalose. Three independent transgenic lines were identified with dominant segregation of the trehalose resistance trait that overexpress the bZIP11 (for basic region/leucine zipper motif) transcription factor. The resistance of these lines to trehalose could not be explained simply through enhanced trehalase activity or through inhibition of bZIP11 translation. Instead, trehalose-6-phosphate (T6P) accumulation was much increased in bZIP11-overexpressing lines, suggesting that these lines may be insensitive to the effects of T6P. T6P is known to inhibit the central stress-integrating kinase SnRK1 (KIN10) activity. We confirmed that this holds true in extracts from seedlings grown on trehalose, then showed that two independent transgenic lines overexpressing KIN10 were insensitive to trehalose. Moreover, the expression of marker genes known to be jointly controlled by SnRK1 activity and bZIP11 was consistent with low SnRK1 or bZIP11 activity in seedlings on trehalose. These results reveal an astonishing case of primary metabolite control over growth by way of the SnRK1 signaling pathway involving T6P, SnRK1, and bZIP11.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The trehalose 6-phosphate/SnRK1 signaling pathway primes growth recovery following relief of sink limitation.Plant Physiol. 2013 Jul;162(3):1720-32. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.220657. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23735508 Free PMC article.
-
Peach PpSnRK1α interacts with bZIP11 and maintains trehalose balance in plants.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021 Mar;160:377-385. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.01.036. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33550178
-
Trehalose 6-phosphate is required for the onset of leaf senescence associated with high carbon availability.Plant Physiol. 2012 Mar;158(3):1241-51. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.191908. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22247267 Free PMC article.
-
How do sugars regulate plant growth and development? New insight into the role of trehalose-6-phosphate.Mol Plant. 2013 Mar;6(2):261-74. doi: 10.1093/mp/sss120. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Mol Plant. 2013. PMID: 23100484 Review.
-
Metabolism control over growth: a case for trehalose-6-phosphate in plants.J Exp Bot. 2012 May;63(9):3379-90. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err311. Epub 2011 Nov 4. J Exp Bot. 2012. PMID: 22058405 Review.
Cited by
-
EXO modifies sucrose and trehalose responses and connects the extracellular carbon status to growth.Front Plant Sci. 2013 Jun 25;4:219. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00219. eCollection 2013. Front Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23805150 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of fruit and seed response to heat and drought by sugars as nutrients and signals.Front Plant Sci. 2013 Aug 1;4:282. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00282. eCollection 2013. Front Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23914195 Free PMC article.
-
Sucrose-induced stomatal closure is conserved across evolution.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 12;13(10):e0205359. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205359. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30312346 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Study Supports the Role of Trehalose in Carbon Transfer From Fungi to Mycotrophic Orchid.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Dec 9;12:793876. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.793876. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34956293 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between sugar and hormone signaling pathways modulate floral signal transduction.Front Genet. 2014 Aug 13;5:218. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00218. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 25165468 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen HM, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al. (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Baena-González E. (2010) Energy signaling in the regulation of gene expression during stress. Mol Plant 3: 300–313 - PubMed
-
- Baena-González E, Rolland F, Thevelein JM, Sheen J. (2007) A central integrator of transcription networks in plant stress and energy signalling. Nature 448: 938–942 - PubMed
-
- Bitrián M, Roodbarkelari F, Horváth M, Koncz C. (2011) BAC-recombineering for studying plant gene regulation: developmental control and cellular localization of SnRK1 kinase subunits. Plant J 65: 829–842 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

