Combustion-derived nanoparticulate induces the adverse vascular effects of diesel exhaust inhalation
- PMID: 21753226
- PMCID: PMC3205591
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr195
Combustion-derived nanoparticulate induces the adverse vascular effects of diesel exhaust inhalation
Abstract
Aim: Exposure to road traffic and air pollution may be a trigger of acute myocardial infarction, but the individual pollutants responsible for this effect have not been established. We assess the role of combustion-derived-nanoparticles in mediating the adverse cardiovascular effects of air pollution.
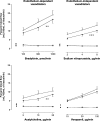
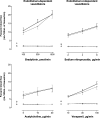
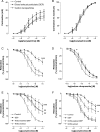
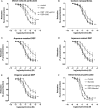
Methods and results: To determine the in vivo effects of inhalation of diesel exhaust components, 16 healthy volunteers were exposed to (i) dilute diesel exhaust, (ii) pure carbon nanoparticulate, (iii) filtered diesel exhaust, or (iv) filtered air, in a randomized double blind cross-over study. Following each exposure, forearm blood flow was measured during intra-brachial bradykinin, acetylcholine, sodium nitroprusside, and verapamil infusions. Compared with filtered air, inhalation of diesel exhaust increased systolic blood pressure (145 ± 4 vs. 133 ± 3 mmHg, P< 0.05) and attenuated vasodilatation to bradykinin (P= 0.005), acetylcholine (P= 0.008), and sodium nitroprusside (P< 0.001). Exposure to pure carbon nanoparticulate or filtered exhaust had no effect on endothelium-dependent or -independent vasodilatation. To determine the direct vascular effects of nanoparticulate, isolated rat aortic rings (n= 6-9 per group) were assessed in vitro by wire myography and exposed to diesel exhaust particulate, pure carbon nanoparticulate and vehicle. Compared with vehicle, diesel exhaust particulate (but not pure carbon nanoparticulate) attenuated both acetylcholine (P< 0.001) and sodium-nitroprusside (P= 0.019)-induced vasorelaxation. These effects were partially attributable to both soluble and insoluble components of the particulate.
Conclusion: Combustion-derived nanoparticulate appears to predominately mediate the adverse vascular effects of diesel exhaust inhalation. This provides a rationale for testing environmental health interventions targeted at reducing traffic-derived particulate emissions.
Figures
Comment in
-
From bench to policies: ready for a nanoparticle air quality standard?Eur Heart J. 2011 Nov;32(21):2613-5. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr200. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Eur Heart J. 2011. PMID: 21753227 No abstract available.
References
-
- Brook RD, Rajagopalan S, Pope CA, III, Brook JR, Bhatnagar A, Diez-Roux AV, Holguin F, Hong Y, Luepker RV, Mittleman MA, Peters A, Siscovick D, Smith SC, Whitsel L, Kaufman JD. Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: an update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121:2331–2378. - PubMed
-
- Pope CA, III, Muhlestein JB, May HT, Renlund DG, Anderson JL, Horne BD. Ischemic heart disease events triggered by short-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. Circulation. 2006;114:2443–2448. - PubMed
-
- Peters A, Dockery DW, Muller JE, Mittleman MA. Increased particulate air pollution and the triggering of myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2001;103:2810–2815. - PubMed
-
- Kwon HJ, Cho SH, Nyberg F, Pershagen G. Effects of ambient air pollution on daily mortality in a cohort of patients with congestive heart failure. Epidemiology. 2001;12:413–419. - PubMed
-
- Miller KA, Siscovick DS, Sheppard L, Shepherd K, Sullivan JH, Anderson GL, Kaufman JD. Long-term exposure to air pollution and incidence of cardiovascular events in women. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:447–458. - PubMed

