Particle size reduction to the nanometer range: a promising approach to improve buccal absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs
- PMID: 21753876
- PMCID: PMC3131191
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S19151
Particle size reduction to the nanometer range: a promising approach to improve buccal absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs
Abstract
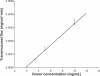
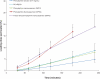
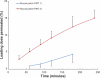
Poorly water-soluble drugs, such as phenylephrine, offer challenging problems for buccal drug delivery. In order to overcome these problems, particle size reduction (to the nanometer range) and cyclodextrin complexation were investigated for permeability enhancement. The apparent solubility in water and the buccal permeation of the original phenylephrine coarse powder, a phenylephrine-cyclodextrin complex and phenylephrine nanosuspensions were characterized. The particle size and particle surface properties of phenylephrine nanosuspensions were used to optimize the size reduction process. The optimized phenylephrine nanosuspension was then freeze dried and incorporated into a multi-layered buccal patch, consisting of a small tablet adhered to a mucoadhesive film, yielding a phenylephrine buccal product with good dosage accuracy and improved mucosal permeability. The design of the buccal patch allows for drug incorporation without the need to change the mucoadhesive component, and is potentially suited to a range of poorly water-soluble compounds.
Keywords: buccal drug delivery; mucoadhesion; nanosuspension; permeation enhancement; solubility.
Figures
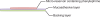
Similar articles
-
Formulation and evaluation of mucoadhesive buccal films impregnated with carvedilol nanosuspension: a potential approach for delivery of drugs having high first-pass metabolism.Drug Deliv. 2013 Jun-Jul;20(5):224-35. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2013.779331. Epub 2013 May 8. Drug Deliv. 2013. PMID: 23651066
-
Dermal flurbiprofen nanosuspensions: Optimization with design of experiment approach and in vitro evaluation.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018 Sep 15;122:254-263. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 29981401
-
Cyclodextrin-containing poly(ethyleneoxide) tablets for the delivery of poorly soluble drugs: potential as buccal delivery system.Int J Pharm. 2006 Aug 17;319(1-2):63-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.03.031. Epub 2006 Apr 25. Int J Pharm. 2006. PMID: 16650700
-
Drug permeation through biomembranes: cyclodextrins and the unstirred water layer.Pharmazie. 2012 May;67(5):363-70. Pharmazie. 2012. PMID: 22764564 Review.
-
Nanosuspension-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Topical Applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jan 25;19:825-844. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S447429. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38293608 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Short-term efficacy of ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide in peripheral neuropathic pain.Pain Res Treat. 2014;2014:854560. doi: 10.1155/2014/854560. Epub 2014 May 20. Pain Res Treat. 2014. PMID: 24967102 Free PMC article.
-
Silver nanoparticles biogenically synthesised using Maclurodendron porteri extract and their bioactivities.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 12;10(4):e25454. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25454. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38379964 Free PMC article.
-
Bioavailability Enhancement and Formulation Technologies of Oral Mucosal Dosage Forms: A Review.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jan 22;17(2):148. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020148. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40006515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano-chitosan-coated, green-synthesized selenium nanoparticles as a novel antifungal agent against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum: in vitro study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 6;15(1):1004. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79574-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39762311 Free PMC article.
-
Development of intramammary delivery systems containing lasalocid for the treatment of bovine mastitis: impact of solubility improvement on safety, efficacy, and milk distribution in dairy cattle.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jan 22;9:631-42. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S74731. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25653501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sudhakar Y, Kuotsu K, Bandyopadhyay AK. Buccal bioadhesive drug delivery – a promising option for orally less efficient drugs. J Control Release. 2006;114(1):15–40. - PubMed
-
- Pather SI, Rathbone MJ, Senel S. Current status and the future of buccal drug delivery systems. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2008;5(6):531–542. - PubMed
-
- Walton RP. Sublingual administration of drugs. J Am Med Assoc. 1944;124(3):138–143.
-
- Bickel MH, Weder HJ. Buccal absorption and other properties of pharmacokinetic importance of imipramine and its metabolites. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1969;21(3):160–168. - PubMed
-
- Lipinski C. Poor aqueous solubility – an industry wide problem in drug discovery. Am Pharm Rev. 2002;(5):82–85.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

