Biochemical markers of contamination in fish toxicity tests
- PMID: 21753904
- PMCID: PMC3131679
- DOI: 10.2478/v10102-011-0015-9
Biochemical markers of contamination in fish toxicity tests
Abstract
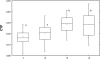
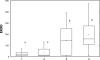
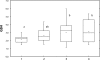
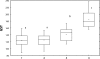
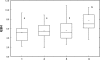
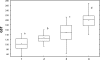
Markers of xenobiotic metabolization (cytochrome P450, ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase, glutathione and glutathione-S-transferase) were investigated in the liver of the common carp Cyprinus carpio after 28-day exposure to different pesticide formulations.The fish exposed to herbicide Sencor 70 WG (metribuzin 700 g/kg) of 0.25 and 2.5 mg/l showed no change in cytochrome P450 and activity of ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase when compared to control.Successor 600 (pethoxamid 600 g/l) of 0.06; 0.22 and 0.60 mg/l did not affect either cytochrome P450 or the activity of ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase. However, in fish exposed to Successor 600 of 0.22 and 0.60 mg/l, there was a rise in glutathione and in the activity of glutathione-S-transferase (p<0.05), with Spearman's correlation r = 0.23 at p<0.05.Spartakus (prochloraz 450 g/l) of 0.36 and 1.08 mg/l induced cytochrome P450 and ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (p<0.05), with Spearman's correlation r=0.49 at p<0.01. Glutathione increased in fish exposed to 1.08 mg/l (p<0.05), the activity of glutathione-S-transferase rose (p<0.05) in all concentrations tested (0.108; 0.36 and 1.08 mg/l). Spearman's correlation between glutathione and GST was r=0.38; p<0.01).The obtained data contribute to a better understanding of detoxification of the selected xenobitics in fish. Although biomarkers of the first phase of metabolization are considered to be more sensitive, our results indicate higher sensitivity of the second phase biomarkers.
Keywords: CYP; EROD; GSH; GST; fish.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of subchronic exposure to Successor 600 (pethoxamid 600 g L-1) on common carp Cyprinus carpio.Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2009;30 Suppl 1:230-5. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2009. PMID: 20027176
-
The effects of Click 500 SC (terbuthylazine) on common carp Cyprinus carpio under (sub)chronic conditions.Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2011;32 Suppl 1:15-24. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2011. PMID: 22167222
-
Biomarkers of Contaminant Exposure in Chub (Leuciscus cephalus L.) - Biomonitoring of Major Rivers in the Czech Republic.Sensors (Basel). 2008 Apr 11;8(4):2589-2603. doi: 10.3390/s8042589. Sensors (Basel). 2008. PMID: 27879837 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the sublethal toxicity of organochlorine pesticide endosulfan in juvenile common carp (Cyprinus carpio).J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2012;47(11):1652-8. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2012.687236. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2012. PMID: 22702825
-
A meta-analytic review of fish antioxidant defense and biotransformation systems following pesticide exposure.Chemosphere. 2022 Mar;291(Pt 1):132730. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132730. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 34743868
Cited by
-
Effect of heavy metals on tissue-specific antioxidant response in Indian major carps.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Aug;24(22):18010-18024. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9415-5. Epub 2017 Jun 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28624940
References
-
- Babin M, Casado S, Chana A, Herradon B, Segner H, Tarazona JV, Navas JM. Cytochrome P4501A induction caused by the imidazole derivative prochloraz in a rainbow trout cell line. Toxicol in vitro. 2005;19:899–902. - PubMed
-
- Balendiran GK, Dabur R, Fraser D. The role of glutathione in cancer. Cell Biochem Funct. 2004;22:343–352. - PubMed
-
- Blanchette B, Feng X, Singh BR. Marine glutathione S-transferases. Mar Biotechnol. 2007;9:513–542. - PubMed
-
- Bleeke MS, Smith MT, Casida JE. Metabolism and toxicity of metribuzin in mouse liver. Pest Biochem Physiol. 1985;23:123–130.
-
- Chang TKH, Waxman DJ. Enzymatic analysis of cDNA-expressed human CYP1A1, CYP1A2, and CYP1B1 with 7-ethoxyresorufin as a substrate. In: Phillips IR, Shephard EA, editors. Cytochrome P450 protocols (Methods in Molecular Biology) Totowa, NJ: Humana Press Inc; 1998. pp. 103–109. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
