(2E,25E)-11,14,17,33,36,39,42-Hepta-oxa-penta-cyclo-[41.4.0.0.0.0]hepta-tetra-conta-1(43),2,5(10),6,8,18,20,22,25,27,29,31,44,46-tetra-decaene-4,24-dione
- PMID: 21754440
- PMCID: PMC3089172
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811013201
(2E,25E)-11,14,17,33,36,39,42-Hepta-oxa-penta-cyclo-[41.4.0.0.0.0]hepta-tetra-conta-1(43),2,5(10),6,8,18,20,22,25,27,29,31,44,46-tetra-decaene-4,24-dione
Abstract
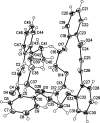
The title compound, C(40)H(40)O(9), is a product of the double crotonic condensation of bis-(2-acetyl-phen-oxy)-3-oxapentane with bis-(2-formyl-phen-oxy)-3,6-dioxaoctane. The title macromolecule includes the 31-crown-7-ether skeletal unit and adopts a saddle-like conformation. The two ethyl-ene fragments have E configurations. The volume of the inter-nal cavity of the macrocycle is approximately 125 Å(3). In the crystal, the mol-ecules are arranged at van der Waals distances.
Figures

References
-
- Anh, L. T., Levov, A. N., Soldatenkov, A. T., Gruzdev, R. D. & Hieu, T. H. (2008). Russ. J. Org. Chem 44, 463–465.
-
- Bradshaw, J. S. & Izatt, R. M. (1997). Acc. Chem. Res. 30, 338–345.
-
- Bruker (1998). SMART and SAINT-Plus Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Gokel, G. W. & Murillo, O. (1996). Acc. Chem. Res. 29, 425–432.
-
- Hiraoka, M. (1978). In Crown Compounds: Their Characteristics and Application Tokyo: Kodansha.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
