4-{2-[2-(4-Chloro-benzyl-idene)hydrazinyl-idene]-3,6-dihydro-2H-1,3,4-thia-diazin-5-yl}-3-phenyl-sydnone
- PMID: 21754481
- PMCID: PMC3089094
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811013912
4-{2-[2-(4-Chloro-benzyl-idene)hydrazinyl-idene]-3,6-dihydro-2H-1,3,4-thia-diazin-5-yl}-3-phenyl-sydnone
Abstract
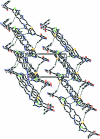
The title compound, C(18)H(13)ClN(6)O(2)S, exists in trans and cis configurations with respect to the acyclic C=N bonds [C=N = 1.2837 (15) and 1.3000 (14) Å, respectively]. The 3,6-dihydro-2H-1,3,4-thia-diazine ring adopts a half-boat conformation. The sydnone ring is approximately planar [maximum deviation = 0.002 (1) Å] and forms dihedral angles of 50.45 (7) and 61.21 (6)° with the aromatic rings. In the crystal, inter-molecular N-H⋯N, C-H⋯Cl and C-H⋯S hydrogen bonds link the mol-ecules into layers parallel to ab plane. The crystal packing is stabilized by C-H⋯π inter-actions and further consolidated by π-π inter-actions involving the phenyl rings [centroid-centroid distance = 3.6306 (7) Å].
Figures
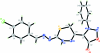
References
-
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
-
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Cosier, J. & Glazer, A. M. (1986). J. Appl. Cryst. 19, 105–107.
-
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
