7,9-Bis(hy-droxy-meth-yl)-7H-purine-2,6,8(1H,3H,9H)trione
- PMID: 21754831
- PMCID: PMC3120625
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811018186
7,9-Bis(hy-droxy-meth-yl)-7H-purine-2,6,8(1H,3H,9H)trione
Abstract
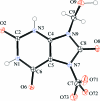
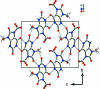
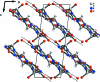
The structure of the title uric acid derivative, C(7)H(8)N(4)O(5), from human kidney stones, is characterized by the C and O atoms of one of the two hy-droxy-methyl groups being disordered nearly equally over three different sites. In the crystal, mol-ecules are connected by a three-dimensional hydrogen-bonding scheme though they look stacked in planes nearly parallel to ([Formula: see text]04).
Figures
References
-
- Ashihara, H., Sano, H. & Crozier, A. (2008). Phytochemistry, 69, 841–846. - PubMed
-
- Brandenburg, K. (2001). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
-
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
-
- Jungers, P., Joly, D., Barbey, F., Choukroun, G. & Daudon, M. (2005). Nephrol. Ther. 1, 301–315. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
