Bacillus amyloliquefaciens G1: A Potential Antagonistic Bacterium against Eel-Pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila
- PMID: 21754944
- PMCID: PMC3132486
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/824104
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens G1: A Potential Antagonistic Bacterium against Eel-Pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila
Abstract
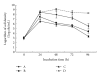
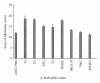
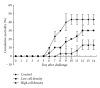
Recent studies have revealed that the use of probiotics is an alternative to control marine aeromonas. However, few probiotics are available against Aeromonas hydrophila infections in eels. In the present study, a potential antagonistic strain G1 against the eel-pathogenic A. hydrophila was isolated from sediment underlying brackish water. Its extracellular products with antibacterial activities were shown to be stable under wide range of pH, temperature, and proteinase K. It was initially identified as Bacillus amyloliquefaciens using API identification kits and confirmed to be B. amyloliquefaciens strain (GenBank accession number DQ422953) by phylogenetic analysis. In addition, it was shown to be safe for mammalians, had a wide anti-A. hydrophila spectrum, and exhibited significant effects on inhibiting the growth of the eel-pathogenic A. hydrophila both in vitro and in vivo. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on a promising antagonistic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain from brackish water sediment against eel-pathogenic A. hydrophila.
Figures

References
-
- Lee WC, Chen YH, Liao IC. The competitiveness of the eel aquaculture in Taiwan, Japan, and China. Aquaculture. 2003;221(1–4):115–124.
-
- Dezfuli BS, Szekely C, Giovinazzo G, Hills K, Giari L. Inflammatory response to parasitic helminths in the digestive tract of Anguilla anguilla (L.) Aquaculture. 2009;296(1-2):1–6.
-
- Daskalov H. The importance of Aeromonas hydrophila in food safety. Food Control. 2006;17(6):474–483.
-
- Fan HP. New diseases and control techniques in the eel farming. Scientific Fish Farming. 2007;7:49–50.
-
- Harikrishnan R, Balasundaram C, Heo M. Effect of probiotics enriched diet on Paralichthys olivaceus infected with lymphocystis disease virus (LCDV) Fish & Shellfish Immunology. 2010;29:868–874. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

