Sensory perception and aging in model systems: from the outside in
- PMID: 21756108
- PMCID: PMC4180250
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154240
Sensory perception and aging in model systems: from the outside in
Abstract
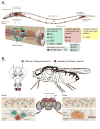
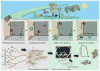
Sensory systems provide organisms from bacteria to humans with the ability to interact with the world. Numerous senses have evolved that allow animals to detect and decode cues from sources in both their external and internal environments. Recent advances in understanding the central mechanisms by which the brains of simple organisms evaluate different cues and initiate behavioral decisions, coupled with observations that sensory manipulations are capable of altering organismal lifespan, have opened the door for powerful new research into aging. Although direct links between sensory perception and aging have been established only recently, here we discuss these initial discoveries and evaluate the potential for different forms of sensory processing to modulate lifespan across taxa. Harnessing the neurobiology of simple model systems to study the biological impact of sensory experiences will yield insights into the broad influence of sensory perception in mammals and may help uncover new mechanisms of healthy aging.
Figures
References
-
- Alcedo J, Kenyon C. Regulation of C. elegans longevity by specific gustatory and olfactory neurons. Neuron. 2004;41:45–55. Reports lifespan of C. elegans following ablation of chemotaxis amphid neurons individually and in combinations. - PubMed
-
- Apfeld J, Kenyon C. Regulation of lifespan by sensory perception in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1999;402:804–9. The first report of a direct connection between sensory input and lifespan regulation. - PubMed
-
- Aristotle De Anima (On the soul) 350 B C
-
- Ashrafi K, Chang FY, Watts JL, Fraser AG, Kamath RS, et al. Genome-wide RNAi analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans fat regulatory genes. Nature. 2003;421:268–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

