Allostasis and allostatic load in the context of poverty in early childhood
- PMID: 21756436
- PMCID: PMC4167021
- DOI: 10.1017/S0954579411000344
Allostasis and allostatic load in the context of poverty in early childhood
Abstract
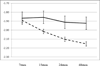
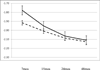
This paper examined the relation of early environmental adversity associated with poverty to child resting or basal level of cortisol in a prospective longitudinal sample of 1135 children seen at 7, 15, 24, 35, and 48 months of age. We found main effects for poor housing quality, African American ethnicity, and low positive caregiving behavior in which each was uniquely associated with an overall higher level of cortisol from age 7 to 48 months. We also found that two aspects of the early environment in the context of poverty, adult exits from the home and perceived economic insufficiency, were related to salivary cortisol in a time-dependent manner. The effect for the first of these, exits from the home, was consistent with the principle of allostatic load in which the effects of adversity on stress physiology accumulate over time. The effect for perceived economic insufficiency was one in which insufficiency was associated with higher levels of cortisol in infancy but with a typical but steeper decline in cortisol with age at subsequent time points.
Figures
References
-
- Arnsten AF, Li BM. Neurobiology of executive functions: Catecholamine influences on prefrontal cortical functions. Biological Psychiatry. 2005;57(11):1377–1384. - PubMed
-
- Bayley N. Manual for Bayley scales of in/ant development. New York: Psychological Corporation; 1969.
-
- Belsky J. Theory testing, effect-size evaluation, and differential susceptibility to rearing influence: The case of mothering and attachment. Child Development. 1997;68(4):598–600. - PubMed
-
- Belsky J, Pluess M. Beyond diathesis stress: Differential susceptibility to environmental influences. Psychological Bulletin. 2009;135(6):885–908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

