Sphingosine kinase-2 inhibition improves mitochondrial function and survival after hepatic ischemia-reperfusion
- PMID: 21756852
- PMCID: PMC3220779
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.05.025
Sphingosine kinase-2 inhibition improves mitochondrial function and survival after hepatic ischemia-reperfusion
Abstract
Background & aims: The mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT) and inflammation play important roles in liver injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion (IR). This study investigated the roles of sphingosine kinase-2 (SK2) in mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation after hepatic IR.
Methods: Mice were gavaged with vehicle or ABC294640 (50 mg/kg), a selective inhibitor of SK2, 1 h before surgery and subjected to 1 h-warm ischemia to ~70% of the liver followed by reperfusion.
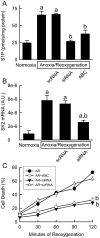
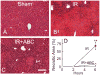
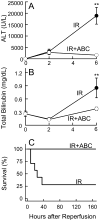
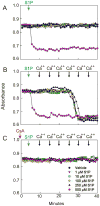
Results: Following IR, hepatic SK2 mRNA and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) levels increased ~25- and 3-fold, respectively. SK2 inhibition blunted S1P production and liver injury by 54-91%, and increased mouse survival from 28% to 100%. At 2 h after reperfusion, mitochondrial depolarization was observed in 74% of viable hepatocytes, and mitochondrial voids excluding calcein disappeared, indicating MPT onset in vivo. SK2 inhibition decreased mitochondrial depolarization and prevented MPT onset. Inducible nitric oxide synthase, phosphorylated NFκB-p65, TNFα mRNA, and neutrophil infiltration, all increased markedly after hepatic IR, and these increases were blunted by SK2 inhibition. In cultured hepatocytes, anoxia/re-oxygenation resulted in increases of SK2 mRNA, S1P levels, and cell death. SK2 siRNA and ABC294640 each substantially decreased S1P production and cell death in cultured hepatocytes.
Conclusions: SK2 plays an important role in mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation responses, hepatocyte death, and survival after hepatic IR and represents a new target for the treatment of IR injury.
Copyright © 2011 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Morales A, Lee H, Goni FM, Kolesnick R, Fernandez-Checa JC. Sphingolipids and cell death. Apoptosis. 2007 May;12(5):923–939. - PubMed
-
- Hait NC, Oskeritzian CA, Paugh SW, Milstien S, Spiegel S. Sphingosine kinases, sphingosine 1-phosphate, apoptosis and diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Dec;1758(12):2016–2026. - PubMed
-
- Olivera A, Spiegel S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate as second messenger in cell proliferation induced by PDGF and FCS mitogens. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):557–560. - PubMed
-
- Lai WQ, Irwan AW, Goh HH, Howe HS, Yu DT, Valle-Onate R, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of sphingosine kinase modulation in inflammatory arthritis. J Immunol. 2008 Dec 1;181(11):8010–8017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

