Interaction between loop diuretic-associated mortality and blood urea nitrogen concentration in chronic heart failure
- PMID: 21757114
- PMCID: PMC3980479
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.01.052
Interaction between loop diuretic-associated mortality and blood urea nitrogen concentration in chronic heart failure
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to investigate whether a surrogate for renal neurohormonal activation, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), could identify patients destined to experience adverse outcomes associated with the use of high-dose loop diuretics (HDLD).
Background: Loop diuretics are commonly used to control congestive symptoms in heart failure; however, these agents cause neurohormonal activation and have been associated with worsened survival.
Methods: Subjects in the BEST (Beta-Blocker Evaluation of Survival Trial) receiving loop diuretics at baseline were analyzed (N = 2,456). The primary outcome was the interaction between BUN- and HDLD-associated mortality.
Results: In the overall cohort, HDLD use (≥160 mg/day) was associated with increased mortality (hazard ratio [HR]: 1.56; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.35 to 1.80). However, after extensively controlling for baseline characteristics, this association did not persist (HR: 1.06; 95% CI: 0.89 to 1.25). In subjects with BUN levels above the median (21.0 mg/dl), both the unadjusted (HR: 1.59; 95% CI: 1.34 to 1.88) and adjusted (HR: 1.29; 95% CI: 1.07 to 1.60) risk of death was higher in the HDLD group. In patients with BUN levels below the median, there was no associated risk with HDLD (HR: 0.99; 95% CI: 0.75 to 1.34) and after controlling for baseline characteristics, the HDLD group had significantly improved survival (HR: 0.71; 95% CI: 0.49 to 0.96) (p interaction = 0.018).
Conclusions: The risk associated with HDLD use is strongly dependent on BUN concentrations with reduced survival in patients with an elevated BUN level and improved survival in patients with a normal BUN level. These data suggest a role for neurohormonal activation in loop diuretic-associated mortality.
Copyright © 2011 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
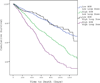
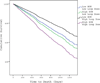
Comment in
-
Blood urea nitrogen a marker for adverse effects of loop diuretics?J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Jul 19;58(4):383-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.01.054. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21757115 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hunt SA, Abraham WT, Chin MH, Feldman AM, Francis GS, Ganiats TG, et al. 2009 Focused update incorporated into the ACC/AHA 2005 Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Heart Failure in Adults A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines Developed in Collaboration With the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J.Am.Coll.Cardiol. 2009 Apr 14;53(15):e1–e90. - PubMed
-
- Francis GS, Benedict C, Johnstone DE, Kirlin PC, Nicklas J, Liang CS, et al. Comparison of neuroendocrine activation in patients with left ventricular dysfunction with and without congestive heart failure. A substudy of the Studies of Left Ventricular Dysfunction (SOLVD) Circulation. 1990 Nov;82(5):1724–1729. - PubMed
-
- Francis GS, Siegel RM, Goldsmith SR, Olivari MT, Levine TB, Cohn JN. Acute vasoconstrictor response to intravenous furosemide in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. Activation of the neurohumoral axis. Ann.Intern.Med. 1985 Jul;103(1):1–6. - PubMed
-
- Cooper HA, Dries DL, Davis CE, Shen YL, Domanski MJ. Diuretics and risk of arrhythmic death in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. Circulation. 1999 Sep 21;100(12):1311–1315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

