Fine-tuning of the Msn2/4-mediated yeast stress responses as revealed by systematic deletion of Msn2/4 partners
- PMID: 21757539
- PMCID: PMC3164460
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-12-1007
Fine-tuning of the Msn2/4-mediated yeast stress responses as revealed by systematic deletion of Msn2/4 partners
Abstract
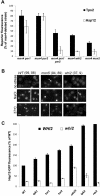
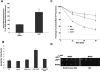
The Msn2 and Msn4 transcription factors play major roles in the yeast general stress response by mediating the transcription of hundreds of genes. Despite extensive information on Msn2/4-mediated gene expression profiles, much less is known regarding the network of proteins that regulate its activity. Here we describe a systematic approach designed to examine the roles of 35 Msn2/4 partners in regulating Msn2/4 transcriptional activity in the face of four different environmental conditions. Our analysis indicates that single deletions of 26 Msn2/4 partners significantly affect Msn2/4 transcription activity under four different conditions. The low functional redundancy of the Msn2 regulatory network indicates that Msn2/4 activity is finely tuned by many of Msn2/4 partners to provide an optimized stress response through differential activation, nuclear localization, degradation, and chromatin remodeling. Our specific analysis of Msn2 activity showed that a relatively large number of partners act to suppress Msn2 activity under nonstress conditions through independent mechanisms, including cytoplasmic retention, proteosome-mediated Msn2 degradation, and chromatin remodeling. Such negative regulation is crucial to minimize the cost of uncontrolled stress response gene expression and ensures a high growth rate in the absence of stress.
Figures






References
-
- Barkai N, Shilo BZ. Variability and robustness in biomolecular systems. Mol Cell. 2007;28:755–760. - PubMed
-
- Beck T, Hall MN. The TOR signalling pathway controls nuclear localization of nutrient-regulated transcription factors. Nature. 1999;402:689–692. - PubMed
-
- Boone C, Bussey H, Andrews BJ. Exploring genetic interactions and networks with yeast. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:437–449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

