p63 is a suppressor of tumorigenesis and metastasis interacting with mutant p53
- PMID: 21760596
- PMCID: PMC3178431
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2011.81
p63 is a suppressor of tumorigenesis and metastasis interacting with mutant p53
Abstract
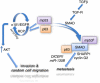
p53 mutations, occurring in two-thirds of all human cancers, confer a gain of function phenotype, including the ability to form metastasis, the determining feature in the prognosis of most human cancer. This effect seems mediated at least partially by its ability to physically interact with p63, thus affecting a cell invasion pathway, and accordingly, p63 is deregulated in human cancers. In addition, p63, as an 'epithelial organizer', directly impinges on epidermal mesenchimal transition, stemness, senescence, cell death and cell cycle arrest, all determinant in cancer, and thus p63 affects chemosensitivity and chemoresistance. This demonstrates an important role for p63 in cancer development and its progression, and the aim of this review is to set this new evidence that links p63 to metastasis within the context of the long conserved other functions of p63.
Figures






References
-
- Yang A, Kaghad M, Wang Y, Gillett E, Fleming MD, Dotsch V, et al. p63, a p53 homolog at 3q27-29, encodes multiple products with transactivating, death-inducing, and dominant-negative activities. Mol Cell. 1998;2:305–316. - PubMed
-
- Schmale H, Bambergeric C. A novel protein with strong homology to the tumor suppressor p53. Oncogene. 1997;15:1363–1366. - PubMed
-
- Trink B, Okami K, Wu L, Spiuranpong V, Jen J, Sidransky D. A new human p53 homolog. Nat Med. 1998;4:747–748. - PubMed
-
- Senoo M, Seiki N, Ohira M, Sugano S, Watanabe M, Tachibana M, et al. A second p53-related protein, p73L, with high homology to p73. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;248:603–607. - PubMed
-
- Senoo M, Seiki N, Ohira M, Sugano S, Watanabe M, Tachibana M, et al. A second p53-related protein, p73L, with high homology to p73. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;248:603–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

