The death receptor CD95 activates the cofilin pathway to stimulate tumour cell invasion
- PMID: 21760611
- PMCID: PMC3166455
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2011.129
The death receptor CD95 activates the cofilin pathway to stimulate tumour cell invasion
Abstract
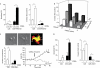
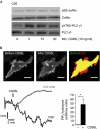
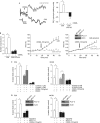
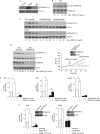
The death receptor CD95 promotes apoptosis through well-defined signalling pathways. In colorectal cancer cells, CD95 primarily stimulates migration and invasion through pathways that are incompletely understood. Here, we identify a new CD95-activated tyrosine kinase pathway that is essential for CD95-stimulated tumour cell invasion. We show that CD95 promotes Tyr 783 phosphorylation of phospholipase C-γ1 through the platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β, resulting in ligand-stimulated phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP(2)) hydrolysis. PIP(2) hydrolysis liberates the actin-severing protein cofilin from the plasma membrane to initiate cortical actin remodelling. Cofilin activation is required for CD95-stimulated formation of membrane protrusions and increased tumour cell invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Andrianantoandro E, Pollard TD (2006) Mechanism of actin filament turnover by severing and nucleation at different concentrations of ADF/cofilin. Mol Cell 24: 13–23 - PubMed
-
- Arber S, Barbayannis FA, Hanser H, Schneider C, Stanyon CA, Bernard O, Caroni P (1998) Regulation of actin dynamics through phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinase. Nature 393: 805–809 - PubMed
-
- Bamburg JR (1999) Proteins of the ADF/cofilin family: essential regulators of actin dynamics. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15: 185–230 - PubMed
-
- Bernard O (2007) Lim kinases, regulators of actin dynamics. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39: 1071–1076 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

