Hfq and its constellation of RNA
- PMID: 21760622
- PMCID: PMC4615618
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro2615
Hfq and its constellation of RNA
Abstract
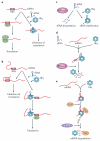
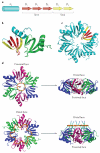
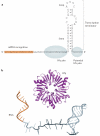
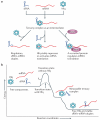
Hfq is an RNA-binding protein that is common to diverse bacterial lineages and has key roles in the control of gene expression. By facilitating the pairing of small RNAs with their target mRNAs, Hfq affects the translation and turnover rates of specific transcripts and contributes to complex post-transcriptional networks. These functions of Hfq can be attributed to its ring-like oligomeric architecture, which presents two non-equivalent binding surfaces that are capable of multiple interactions with RNA molecules. Distant homologues of Hfq occur in archaea and eukaryotes, reflecting an ancient origin for the protein family and hinting at shared functions. In this Review, we describe the salient structural and functional features of Hfq and discuss possible mechanisms by which this protein can promote RNA interactions to catalyse specific and rapid regulatory responses in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Wilusz CJ, Wilusz J. Eukaryotic Lsm proteins: lessons from bacteria. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005;12:1031–1036. - PubMed
-
- Valentin-Hansen P, Eriksen M, Udesen C. The bacterial Sm-like protein Hfq: a key player in RNA transactions. Mol. Microbiol. 2004;51:1525–1533. - PubMed
-
- Chao Y, Vogel J. The role of Hfq in bacterial pathogens. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010;13:24–33. - PubMed
-
- Papenfort K, Vogel J. Regulatory RNA in bacterial pathogens. Cell Host Microbe. 2010;8:116–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

