Role for microRNAs in regulating glucocorticoid response and resistance in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 21761344
- PMCID: PMC3725966
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-011-0072-8
Role for microRNAs in regulating glucocorticoid response and resistance in multiple myeloma
Abstract
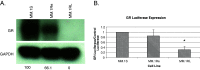
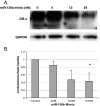
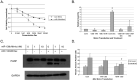
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are widely used in the treatment of hematological malignancies such as multiple myeloma. However, the development of resistance to GCs limits their clinical utility. Response to GCs is dependent on an active glucocorticoid receptor, GR-α, expressed at wild-type levels in the GC-sensitive cell line (MM.1S). GC-resistant derivative cell lines MM.1Re and MM.1RL display significant downregulation of GR-α transcripts. In this study, we report that a luciferase reporter containing the 3'-UTR of GR-α is significantly repressed in MM.1R cells when compared to MM.1S cells, suggesting that one or several microRNAs that are upregulated in MM.1R maybe in part responsible for the downregulation of the GR-α transcript. To examine posttranscriptional mechanisms of GR regulation, we examined miRNAs that have complimentary binding sites in the 3'-UTR of GR-α and found miR-130b, miR-181a, and miR-636 to be differentially expressed between GC-sensitive and GC-resistant MM.1 cell lines. Overexpression of miR-130b in MM.1S cells results in decreased expression of endogenous GR protein and decreased activity of the luciferase reporter. In addition, in MM.1S cells, the downstream GC response of glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper induction is decreased by the overexpression of miR-130b, and further miR-130b inhibits GC-induced apoptosis and causes resistance to GCs.
© Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2011
Figures

References
-
- Greenstein S, Ghias K, Krett NL, Rosen ST. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid-mediated apoptosis in hematological malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:1681–1694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

