Telmisartan and amlodipine single-pill combinations vs amlodipine monotherapy for superior blood pressure lowering and improved tolerability in patients with uncontrolled hypertension: results of the TEAMSTA-5 study
- PMID: 21762357
- PMCID: PMC8108958
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2011.00468.x
Telmisartan and amlodipine single-pill combinations vs amlodipine monotherapy for superior blood pressure lowering and improved tolerability in patients with uncontrolled hypertension: results of the TEAMSTA-5 study
Abstract
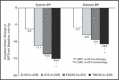
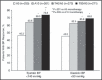
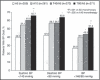
An 8-week, randomized, double-blind, controlled study with single-pill combinations of telmisartan 40 mg or 80 mg/amlodipine 5 mg (T40/A5 or T80/A5) vs monotherapy with amlodipine 5 mg or 10 mg (A10) in 1097 patients with uncontrolled hypertension (diastolic blood pressure [BP] ≥ 90 mm Hg). T40/A5 and T80/A5 resulted in significantly greater (P<.0001) reductions in seated trough systolic/diastolic BP vs A5 (-7.4 mm Hg/-3.6 mm Hg; -8.8 mm Hg/-4.9 mm Hg) and a significantly greater (P<.001) proportion of patients achieving systolic/diastolic BP goal rate (60.0%/56.7%; 65.7%/63.8%) vs A5 (39.2%/42.0%). Superior BP reductions were also seen with T40-T80/A5 vs A10, with BP goal rates at least as high as with A10; however, there was significantly more peripheral edema with A10 (27.2% vs 4.3% for pooled T40-T80/A5; P<.0001). Switching patients with uncontrolled BP to a single-pill combination of T40/A5 or T80/A5 is a better treatment option than up-titration to full-dose monotherapy with A10.
© 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Mancia G, Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. 2007 Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. The Task Force for the management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2007;25:1105–1187. - PubMed
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. The seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–2572. - PubMed
-
- Dahlöf B, Lindholm LH, Carney S, et al. Main results of the losartan versus amlodipine (LOA) study on drug tolerability and psychological general well‐being. LOA Study Group. J Hypertens. 1997;15:1327–1335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

