Tight junction proteins expression and modulation in immune cells and multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 21762372
- PMCID: PMC3822847
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01380.x
Tight junction proteins expression and modulation in immune cells and multiple sclerosis
Abstract
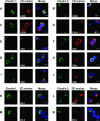
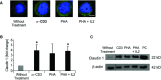
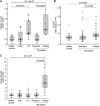
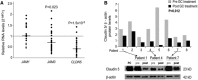
The tight junction proteins (TJPs) are major determinants of endothelial cells comprising physiological vascular barriers such as the blood-brain barrier, but little is known about their expression and role in immune cells. In this study we assessed TJP expression in human leukocyte subsets, their induction by immune activation and modulation associated with autoimmune disease states and therapies. A consistent expression of TJP complexes was detected in peripheral blood leukocytes (PBLs), predominantly in B and T lymphocytes and monocytes, whereas the in vitro application of various immune cell activators led to an increase of claudin 1 levels, yet not of claudin 5. Claudins 1 and 5 levels were elevated in PBLs of multiple sclerosis (MS) patients in relapse, relative to patients in remission, healthy controls and patients with other neurological disorders. Interestingly, claudin 1 protein levels were elevated also in PBLs of patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D). Following glucocorticoid treatment of MS patients in relapse, RNA levels of JAM3 and CLDN5 and claudin 5 protein levels in PBLs decreased. Furthermore, a correlation between CLDN5 pre-treatment levels and clinical response phenotype to interferon-β therapy was detected. Our findings indicate that higher levels of leukocyte claudins are associated with immune activation and specifically, increased levels of claudin 5 are associated with MS disease activity. This study highlights a potential role of leukocyte TJPs in physiological states, and autoimmunity and suggests they should be further evaluated as biomarkers for aberrant immune activity and response to therapy in immune-mediated diseases such as MS.
© 2011 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2011 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007 Apr;27(4):697-709. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600375. Epub 2006 Jul 19. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007. PMID: 16850029
-
Leukocyte Gene Expression and Plasma Concentration in Multiple Sclerosis: Alteration of Transforming Growth Factor-βs, Claudin-11, and Matrix Metalloproteinase-2.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Aug;36(6):865-872. doi: 10.1007/s10571-015-0270-y. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26768647 Free PMC article.
-
Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin fragment removes specific claudins from tight junction strands: Evidence for direct involvement of claudins in tight junction barrier.J Cell Biol. 1999 Oct 4;147(1):195-204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.147.1.195. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10508866 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of claudin tight junction proteins and their complex interactions in various physiological systems.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2010;279:1-32. doi: 10.1016/S1937-6448(10)79001-8. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20797675 Review.
-
Transmembrane proteins in the tight junction barrier.J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999 Jun;10(6):1337-45. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V1061337. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999. PMID: 10361874 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Snail-1, E-cadherin and claudin-1 expression in colorectal adenomas and carcinomas.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(2):1632-1643. doi: 10.3390/ijms13021632. Epub 2012 Feb 2. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22408413 Free PMC article.
-
Bicellular Tight Junctions and Wound Healing.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 4;19(12):3862. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123862. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30518037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Appearance of claudin-5+ leukocytes in the central nervous system during neuroinflammation: a novel role for endothelial-derived extracellular vesicles.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Nov 16;13(1):292. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0755-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27852330 Free PMC article.
-
Claudins and the modulation of tight junction permeability.Physiol Rev. 2013 Apr;93(2):525-69. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00019.2012. Physiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23589827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Teriflunomide Promotes Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity by Upregulating Claudin-1 via the Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway in Multiple Sclerosis.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Apr;61(4):1936-1952. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03655-7. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37819429
References
-
- Balague C, Kunkel SL, Godessart N. Understanding autoimmune disease: new targets for drug discovery. Drug Discov Today. 2009;14:926–34. - PubMed
-
- Weiner HL. The challenge of multiple sclerosis: how do we cure a chronic heterogeneous disease? Ann Neurol. 2009;65:239–48. - PubMed
-
- Prat A, Biernacki K, Lavoie JF, et al. Migration of multiple sclerosis lymphocytes through brain endothelium. Arch Neurol. 2002;59:391–7. - PubMed
-
- Tischner D, Reichardt HM. Glucocorticoids in the control of neuroinflammation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007;275:62–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

