EuroPineDB: a high-coverage web database for maritime pine transcriptome
- PMID: 21762488
- PMCID: PMC3152544
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-366
EuroPineDB: a high-coverage web database for maritime pine transcriptome
Abstract
Background: Pinus pinaster is an economically and ecologically important species that is becoming a woody gymnosperm model. Its enormous genome size makes whole-genome sequencing approaches are hard to apply. Therefore, the expressed portion of the genome has to be characterised and the results and annotations have to be stored in dedicated databases.
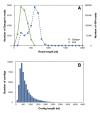
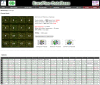
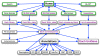
Description: EuroPineDB is the largest sequence collection available for a single pine species, Pinus pinaster (maritime pine), since it comprises 951 641 raw sequence reads obtained from non-normalised cDNA libraries and high-throughput sequencing from adult (xylem, phloem, roots, stem, needles, cones, strobili) and embryonic (germinated embryos, buds, callus) maritime pine tissues. Using open-source tools, sequences were optimally pre-processed, assembled, and extensively annotated (GO, EC and KEGG terms, descriptions, SNPs, SSRs, ORFs and InterPro codes). As a result, a 10.5× P. pinaster genome was covered and assembled in 55 322 UniGenes. A total of 32 919 (59.5%) of P. pinaster UniGenes were annotated with at least one description, revealing at least 18 466 different genes. The complete database, which is designed to be scalable, maintainable, and expandable, is freely available at: http://www.scbi.uma.es/pindb/. It can be retrieved by gene libraries, pine species, annotations, UniGenes and microarrays (i.e., the sequences are distributed in two-colour microarrays; this is the only conifer database that provides this information) and will be periodically updated. Small assemblies can be viewed using a dedicated visualisation tool that connects them with SNPs. Any sequence or annotation set shown on-screen can be downloaded. Retrieval mechanisms for sequences and gene annotations are provided.
Conclusions: The EuroPineDB with its integrated information can be used to reveal new knowledge, offers an easy-to-use collection of information to directly support experimental work (including microarray hybridisation), and provides deeper knowledge on the maritime pine transcriptome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
De novo assembly of maritime pine transcriptome: implications for forest breeding and biotechnology.Plant Biotechnol J. 2014 Apr;12(3):286-99. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12136. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Plant Biotechnol J. 2014. PMID: 24256179
-
Comprehensive assembly and analysis of the transcriptome of maritime pine developing embryos.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Dec 29;18(1):379. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1564-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30594130 Free PMC article.
-
Development and implementation of a highly-multiplexed SNP array for genetic mapping in maritime pine and comparative mapping with loblolly pine.BMC Genomics. 2011 Jul 18;12:368. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-368. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21767361 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and analysis of expressed sequence tags from six developing xylem libraries in Pinus radiata D. Don.BMC Genomics. 2009 Jan 21;10:41. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-41. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19159482 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis in maritime pine using laser capture microdissection and 454 pyrosequencing.Tree Physiol. 2014 Nov;34(11):1278-88. doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpt113. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Tree Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24391165
Cited by
-
Novel insights into regulation of asparagine synthetase in conifers.Front Plant Sci. 2012 May 24;3:100. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00100. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22654888 Free PMC article.
-
Stone Pine (Pinus pinea L.) High-Added-Value Genetics: An Overview.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;15(1):84. doi: 10.3390/genes15010084. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards decoding the conifer giga-genome.Plant Mol Biol. 2012 Dec;80(6):555-69. doi: 10.1007/s11103-012-9961-7. Epub 2012 Sep 9. Plant Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22960864 Review.
-
A SNP resource for Douglas-fir: de novo transcriptome assembly and SNP detection and validation.BMC Genomics. 2013 Feb 28;14:137. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-137. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23445355 Free PMC article.
-
Searching for resistance genes to Bursaphelenchus xylophilus using high throughput screening.BMC Genomics. 2012 Nov 7;13:599. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-599. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23134679 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahuja MR, Neale DB. Evolution of genome size in conifers. Silvae Genetica. 2005;54:126–137.
-
- Alonso P, Cortizo M, Cantón FR, Fernández B, Rodríguez A, Centeno ML, Cánovas FM, Ordás RJ. Identification of genes differentially expressed during adventitious shoot induction in Pinus pinea cotyledons by subtractive hybridization and quantitative PCR. Tree Physiol. 2007;27(12):1721–1730. - PubMed
-
- Paiva JAP, Garnier-Géré PH, Rodrigues JC, Alves A, Santos S, Graça J, Le Provost G, Chaumeil G, Da Silva-Perez D, Bosc A, Fevereiro P, Plomion C. Plasticity of maritime pine (Pinus pinaster) wood-forming tissues during a growing season. New Phytol. 2008;179(4):1080–1094. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

