CM156, a high affinity sigma ligand, attenuates the stimulant and neurotoxic effects of methamphetamine in mice
- PMID: 21762711
- PMCID: PMC3615888
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.06.028
CM156, a high affinity sigma ligand, attenuates the stimulant and neurotoxic effects of methamphetamine in mice
Abstract
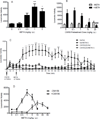
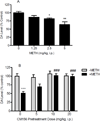
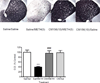
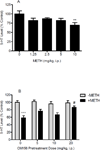
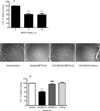
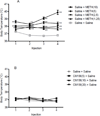
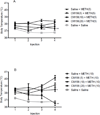
Methamphetamine (METH) is a highly addictive psychostimulant drug of abuse. Low and high dose administration of METH leads to locomotor stimulation, and dopaminergic and serotonergic neurotoxicity, respectively. The behavioral stimulant and neurotoxic effects of METH can contribute to addiction and other neuropsychiatric disorders, thus necessitating the identification of potential pharmacotherapeutics against these effects produced by METH. METH binds to σ receptors at physiologically relevant concentrations. Also, σ receptors are present on and can modulate dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons. Therefore, σ receptors provide a viable target for the development of pharmacotherapeutics against the adverse effects of METH. In the present study, CM156, a σ receptor ligand with high affinity and selectivity for σ receptors over 80 other non-σ binding sites, was evaluated against METH-induced stimulant, hyperthermic, and neurotoxic effects. Pretreatment of male, Swiss Webster mice with CM156 dose dependently attenuated the locomotor stimulation, hyperthermia, striatal dopamine and serotonin depletions, and striatal dopamine and serotonin transporter reductions produced by METH, without significant effects of CM156 on its own. These results demonstrate the ability of a highly selective σ ligand to mitigate the effects of METH.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological evaluation of SN79, a sigma (σ) receptor ligand, against methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity in vivo.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013 Aug;23(8):960-71. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.08.005. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 22921523 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of methamphetamine-induced effects through the antagonism of sigma (sigma) receptors: Evidence from in vivo and in vitro studies.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008 Dec;18(12):871-81. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2008.07.006. Epub 2008 Aug 27. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18755577 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and pharmacological characterization of a novel sigma receptor ligand with improved metabolic stability and antagonistic effects against methamphetamine.AAPS J. 2012 Mar;14(1):43-51. doi: 10.1208/s12248-011-9311-8. Epub 2011 Dec 20. AAPS J. 2012. PMID: 22183188 Free PMC article.
-
Could sigma receptor ligands be a treatment for methamphetamine addiction?Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2010 Sep;3(3):156-62. doi: 10.2174/1874473711003030156. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2010. PMID: 21054260 Review.
-
Involvement of nicotinic receptors in methamphetamine- and MDMA-induced neurotoxicity: pharmacological implications.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009;88:121-66. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7742(09)88006-9. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19897077 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and Synthesis of Veranamine, an Antidepressant Lead from the Marine Sponge Verongula rigida.J Nat Prod. 2020 Apr 24;83(4):1092-1098. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01107. Epub 2020 Mar 31. J Nat Prod. 2020. PMID: 32227883 Free PMC article.
-
Sigma Receptors and Substance Use Disorders.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;964:177-199. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50174-1_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28315272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of sigma-1 receptor with dopamine transporter attenuates the binding of methamphetamine via distinct helix-helix interactions.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021 Jun;97(6):1194-1209. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13841. Epub 2021 Apr 4. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021. PMID: 33754484 Free PMC article.
-
The cross-talk of HIV-1 Tat and methamphetamine in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders.Front Microbiol. 2015 Oct 23;6:1164. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01164. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26557111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective targets through which 6-acetyl-3-(4-(4-(4-fluorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)benzo[d]oxazol-2(3H)-one (SN79), a sigma receptor ligand, mitigates the effects of methamphetamine in vitro.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Feb 5;724:193-203. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.12.039. Epub 2013 Dec 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24380829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bastianetto S, Rouquier L, Perrault G, Sanger DJ. DTG-induced circling behaviour in rats may involve the interaction between sigma sites and nigro-striatal dopaminergic pathways. Neuropharmacology. 1995;34:281–287. - PubMed
-
- Booth RG, Baldessarini RJ. (+)-6,7-Benzomorphan sigma ligands stimulate dopamine synthesis in rat corpus striatum tissue. Brain Res. 1991;557:349–352. - PubMed
-
- Bouchard P, Quirion R. [3H]1,3-di(2-tolyl)guanidine and [3H](+)pentazocine binding sites in the rat brain: autoradiographic visualization of the putative sigma1 and sigma2 receptor subtypes. Neuroscience. 1997;76:467–477. - PubMed
-
- Bowen WD. Sigma receptors: recent advances and new clinical potentials. Pharm. Acta. Helv. 2000;74:211–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

