IL-5 receptor α levels in patients with marked eosinophilia or mastocytosis
- PMID: 21762978
- PMCID: PMC3205313
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.05.032
IL-5 receptor α levels in patients with marked eosinophilia or mastocytosis
Abstract
Background: IL-5 plays a central role in the development and maintenance of eosinophilia (EO) and eosinophil activation in a wide variety of eosinophilic disorders. Although IL-5, IL-3, and GM-CSF can modulate the expression of IL-5 receptor α (IL-5Rα) on eosinophils in vitro, little is known about soluble and surface IL-5Rα levels in vivo.
Objective: To assess soluble and surface IL-5Rα levels in patients with EO and/or mastocytosis.
Methods: Surface IL-5Rα expression was assessed by flow cytometry in blood and/or bone marrow from subjects with EO (n = 39) and systemic mastocytosis (n = 8) and from normal volunteers (n = 28). Soluble IL-5Rα (sIL-5Rα) level was measured in a cohort of 177 untreated subjects and correlated with EO, eosinophil activation, and serum tryptase and cytokine levels.
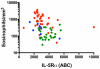
Results: IL-5Rα expression on eosinophils inversely correlated with EO (r = -0.48; P < .0001), whereas serum levels of sIL-5Rα increased with the eosinophil count (r = 0.56; P < .0001) and serum IL-5 (r = 0.40; P < .0001) and IL-13 (r = 0.29; P = .004) levels. Of interest, sIL-5Rα level was significantly elevated in patients with systemic mastocytosis without EO. Although sIL-5Rα levels correlated with serum tryptase levels in these patients, eosinophil activation, assessed by CD69 expression on eosinophils and serum eosinophil-derived neurotoxin levels, was increased compared with that in normal subjects.
Conclusions: These data are consistent with an in vivo IL-5Rα regulatory pathway in human eosinophils similar to that described in vitro and involving a balance between soluble and surface receptor levels. This may have implications with respect to the use of novel therapeutic agents targeting IL-5 and its receptor in patients with EO and/or mastocytosis.
Published by Mosby, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Tavernier J, Devos R, Cornelis S, et al. A human high affinity interleukin-5 receptor (IL5R) is composed of an IL5-specific α chain and a β chain shared with the receptor for GM-CSF. Cell. 1991;66:1175–1184. - PubMed
-
- Rothenberg ME, Klion AD, Roufosse FE, et al. Treatment of patients with the hypereosinophilic syndrome with mepolizumab. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1215–1228. - PubMed
-
- Nair P, Pizzichini MM, Kjarsgaard M, et al. Mepolizumab for prednisone-dependent asthma with sputum eosinophilia. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:985–993. - PubMed
-
- Kolbeck R, Kozhich AA, Koike M, et al. MEDI-563, a humanized anti-IL-5 receptor α mAb with enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity function. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125:1344–1353. - PubMed

