Central sensitization of nociceptive neurons in rat medullary dorsal horn involves purinergic P2X7 receptors
- PMID: 21763757
- PMCID: PMC3172718
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.06.083
Central sensitization of nociceptive neurons in rat medullary dorsal horn involves purinergic P2X7 receptors
Abstract
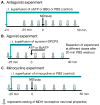
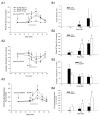
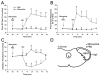
Central sensitization is a crucial process underlying the increased neuronal excitability of nociceptive pathways following peripheral tissue injury and inflammation. Our previous findings have suggested that extracellular adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) molecules acting at purinergic receptors located on presynaptic terminals (e.g., P2X2/3, P2X3 subunits) and glial cells are involved in the glutamatergic-dependent central sensitization induced in medullary dorsal horn (MDH) nociceptive neurons by application to the tooth pulp of the inflammatory irritant mustard oil (MO). Since growing evidence indicates that activation of P2X7 receptors located on glia is involved in chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain, the aim of the present study was to test in vivo for P2X7 receptor involvement in this acute inflammatory pain model. Experiments were carried out in anesthetized Sprague-Dawley male rats. Single unit recordings were made in MDH functionally identified nociceptive neurons for which mechanoreceptive field, mechanical activation threshold and responses to noxious stimuli were tested. We found that continuous intrathecal (i.t.) superfusion over MDH of the potent P2X7 receptor antagonists brilliant blue G and periodated oxidized ATP could each significantly attenuate the MO-induced MDH central sensitization. MDH central sensitization could also be produced by i.t. superfusion of ATP and even more effectively by the P2X7 receptor agonist benzoylbenzoyl ATP. Superfusion of the microglial blocker minocycline abolished the MO-induced MDH central sensitization, consistent with reports that dorsal horn P2X7 receptors are mostly expressed on microglia. In control experiments, superfusion over MDH of vehicle did not produce any significant changes. These novel findings suggest that activation of P2X7 receptors in vivo may be involved in the development of central sensitization in an acute inflammatory pain model.
Copyright © 2011 IBRO. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Involvement of glia in central sensitization in trigeminal subnucleus caudalis (medullary dorsal horn).Brain Behav Immun. 2007 Jul;21(5):634-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2006.07.008. Epub 2006 Oct 20. Brain Behav Immun. 2007. PMID: 17055698
-
Involvement of ATP in noxious stimulus-evoked release of glutamate in rat medullary dorsal horn: a microdialysis study.Neurochem Int. 2012 Dec;61(8):1276-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2012.10.004. Epub 2012 Oct 15. Neurochem Int. 2012. PMID: 23079194 Free PMC article.
-
Central α-adrenoceptors contribute to mustard oil-induced central sensitization in the rat medullary dorsal horn.Neuroscience. 2013 Apr 16;236:244-52. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.01.016. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23333675 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous ATP involvement in mustard-oil-induced central sensitization in trigeminal subnucleus caudalis (medullary dorsal horn).J Neurophysiol. 2005 Sep;94(3):1751-60. doi: 10.1152/jn.00223.2005. Epub 2005 May 18. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 15901761
-
On the Role of ATP-Gated P2X Receptors in Acute, Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain.In: Kruger L, Light AR, editors. Translational Pain Research: From Mouse to Man. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2010. Chapter 10. In: Kruger L, Light AR, editors. Translational Pain Research: From Mouse to Man. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2010. Chapter 10. PMID: 21882468 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
P2X4 purinoceptor signaling in chronic pain.Purinergic Signal. 2012 Sep;8(3):621-8. doi: 10.1007/s11302-012-9306-7. Epub 2012 Apr 15. Purinergic Signal. 2012. PMID: 22528681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of P2X7 Purinergic Receptor Ameliorates Fibromyalgia Syndrome by Suppressing NLRP3 Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 16;22(12):6471. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126471. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34208781 Free PMC article.
-
Descending control of nociception in insects?Proc Biol Sci. 2022 Jul 13;289(1978):20220599. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2022.0599. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Proc Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35858073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible Interaction of Suramin with Thalamic P2X Receptors and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Alleviates Reserpine-Induced Fibromyalgia-Like Symptoms.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025 May 7;20(1):51. doi: 10.1007/s11481-025-10207-4. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40329125 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of microglial P2X7 receptor in pain modulation.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Jan;30(1):e14496. doi: 10.1111/cns.14496. Epub 2023 Nov 10. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37950524 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beindl W, Mitterauer T, Hohenegger M, Ijzerman AP, Nanoff C, Freissmuth M. Inhibition of receptor/G protein coupling by suramin analogues. Mol Pharmacol. 1996;50:415–423. - PubMed
-
- Boyer JL, Harden TK. Irreversible activation of phospholipase C-coupled P2Y-purinergic receptors by 3′-O-(4-benzoyl)benzoyl adenosine 5′-triphosphate. Mol Pharmacol. 1989;36:831–835. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G. Purinergic signalling and disorders of the central nervous system. Nat Rev Drug Disc. 2008;7:575–590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

