HIV-1 Tat-induced cerebrovascular toxicity is enhanced in mice with amyloid deposits
- PMID: 21764480
- PMCID: PMC3206197
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.06.004
HIV-1 Tat-induced cerebrovascular toxicity is enhanced in mice with amyloid deposits
Abstract
HIV-1-infected brains are characterized by elevated depositions of amyloid beta (Aβ); however, the interactions between Aβ and HIV-1 are poorly understood. In the present study, we administered specific HIV-1 protein Tat into the cerebral vasculature of 50-52-week-old double transgenic (B6C3-Tg) mice that express a chimeric mouse/human amyloid precursor protein (Mo/HuAPP695swe) and a mutant human presenilin 1 (PS1-dE9) and are characterized by increased Aβ depositions in the brain. Exposure to Tat increased permeability across cerebral capillaries, enhanced disruption of zonula occludens (ZO)-1 tight junction protein, and elevated brain expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in B6C3-Tg mice as compared with age-matched littermate controls. These changes were associated with increased leukocyte attachment and their transcapillary migration. The majority of Tat-induced effects were attenuated by treatment with a specific Rho inhibitor, hydroxyfasudil. The results of animal experiments were reproduced in cultured brain endothelial cells exposed to Aβ and/or Tat. The present data indicate that increased brain levels of Aβ can enhance vascular toxicity and proinflammatory responses induced by HIV-1 protein Tat.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
No actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
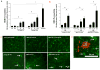
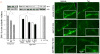

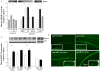
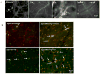
Similar articles
-
Rho-kinase inhibitor hydroxyfasudil protects against HIV-1 Tat-induced dysfunction of tight junction and neprilysin/Aβ transfer receptor expression in mouse brain microvessels.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 May;476(5):2159-2170. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04056-x. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33548010 Free PMC article.
-
Deposition of mouse amyloid beta in human APP/PS1 double and single AD model transgenic mice.Neurobiol Dis. 2006 Sep;23(3):653-62. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2006.05.010. Epub 2006 Jul 10. Neurobiol Dis. 2006. PMID: 16829076
-
Human apolipoprotein E redistributes fibrillar amyloid deposition in Tg-SwDI mice.J Neurosci. 2008 May 14;28(20):5312-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1042-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18480287 Free PMC article.
-
ApoA-I deficiency increases cortical amyloid deposition, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, cortical and hippocampal astrogliosis, and amyloid-associated astrocyte reactivity in APP/PS1 mice.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019 May 13;11(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0497-9. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31084613 Free PMC article.
-
Early-onset formation of parenchymal plaque amyloid abrogates cerebral microvascular amyloid accumulation in transgenic mice.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jun 20;289(25):17895-908. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.536565. Epub 2014 May 14. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24828504 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
PPAR agonist-mediated protection against HIV Tat-induced cerebrovascular toxicity is enhanced in MMP-9-deficient mice.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014 Apr;34(4):646-53. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.240. Epub 2014 Jan 15. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014. PMID: 24424383 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 stimulates nuclear entry of amyloid beta via dynamin dependent EEA1 and TGF-β/Smad signaling.Exp Cell Res. 2014 Apr 15;323(1):66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.01.027. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Exp Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24491918 Free PMC article.
-
Amphiphilic Cell-Penetrating Peptides Containing Natural and Unnatural Amino Acids as Drug Delivery Agents.Cells. 2022 Mar 29;11(7):1156. doi: 10.3390/cells11071156. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406720 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1-Associated Common Neurological Complications: Does Aging Pose a Challenge?J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;60(s1):S169-S193. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170473. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 28800335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV and Alzheimer's disease: complex interactions of HIV-Tat with amyloid β peptide and Tau protein.J Neurovirol. 2019 Oct;25(5):648-660. doi: 10.1007/s13365-019-00736-z. Epub 2019 Apr 23. J Neurovirol. 2019. PMID: 31016584 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41–53. - PubMed
-
- Andras IE, Pu H, Tian J, Deli MA, Nath A, Hennig B, Toborek M. Signaling mechanisms of HIV-1 Tat-induced alterations of claudin-5 expression in brain endothelial cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005;25:1159–1170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH063022/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA027569/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH63022/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES007380/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR15592/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA027569/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- CA133257/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NS39254/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH098891/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH072567/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA133257/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ES007380/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS039254/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH072567/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

