Mutations in NBEAL2, encoding a BEACH protein, cause gray platelet syndrome
- PMID: 21765413
- PMCID: PMC6050511
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.884
Mutations in NBEAL2, encoding a BEACH protein, cause gray platelet syndrome
Abstract
Next-generation RNA sequence analysis of platelets from an individual with autosomal recessive gray platelet syndrome (GPS, MIM139090) detected abnormal transcript reads, including intron retention, mapping to NBEAL2 (encoding neurobeachin-like 2). Genomic DNA sequencing confirmed mutations in NBEAL2 as the genetic cause of GPS. NBEAL2 encodes a protein containing a BEACH domain that is predicted to be involved in vesicular trafficking and may be critical for the development of platelet α-granules.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

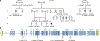
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 DK057516/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL066277/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL066277/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL084086-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL091283/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MOP-81208/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- T32 HL105321/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024979/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK57516/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MOP-84556/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- HL091283/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024979/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

